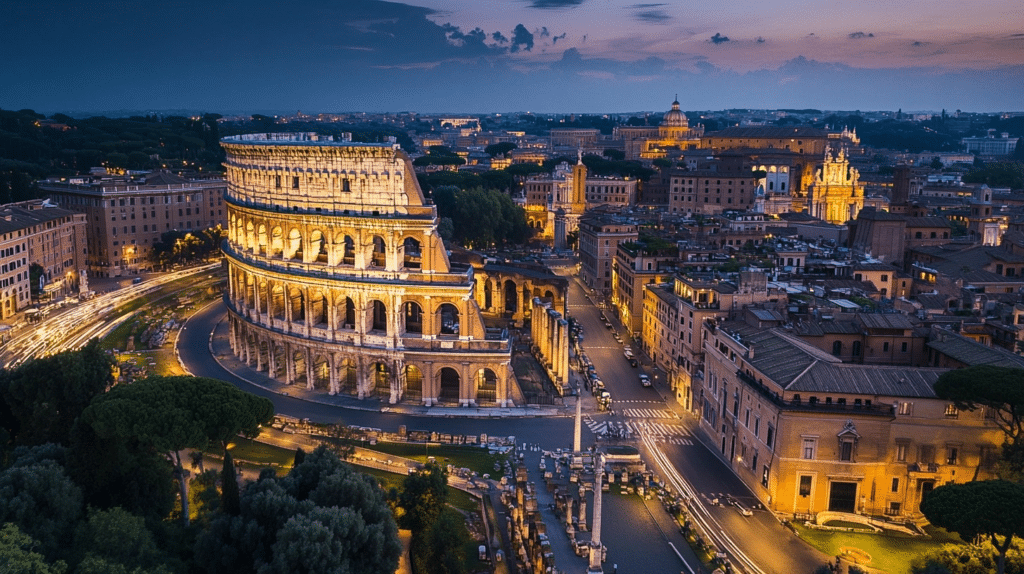
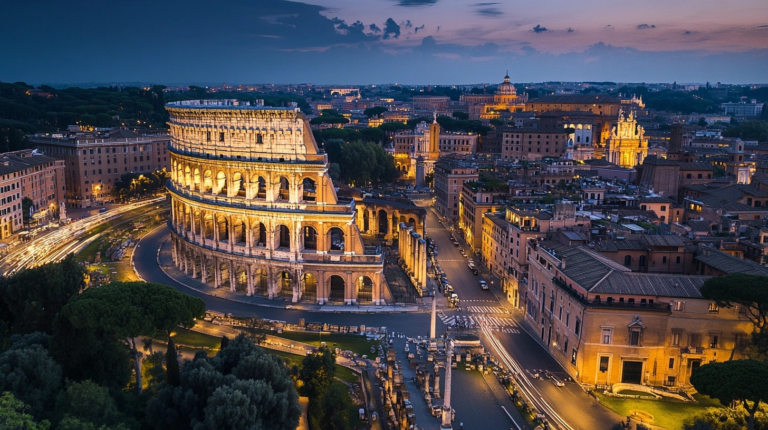
The ancient city of Rome holds secrets that continue to enthrall history buffs worldwide.
From mighty emperors to architectural marvels that still stand today, Rome’s story attracts anyone with even a passing interest in the past.
Many history lovers feel overwhelmed when trying to learn about Rome’s vast legacy. They often miss key facts that make this ancient civilization so remarkable and influential.
This extensive collection of 151 Rome facts solves this problem by offering bite-sized, easy-to-digest information that covers everything from the founding myths to the fall of the empire.
Readers who look into these facts will gain a broader understanding of how Rome shaped modern society and enjoy sharing these interesting tidbits with friends and family.
Why Rome Is Called the Eternal City
Rome has been called the Eternal City for centuries, and there’s a good reason for it!
The nickname comes from ancient Romans who believed that no matter what happened, Rome would always stand strong.
Unlike other great civilizations that faded away, Rome has remained a symbol of power, culture, and history for over 2,000 years.
One of the first people to use this term was the Roman poet Tibullus in the 1st century BC. He described Rome as a city that would never fall, a place that would outlive all empires.
And honestly? He wasn’t wrong! Despite wars, invasions, and changes in rulers, Rome has kept its charm and influence through the ages.
From the ruins of the Colosseum to the occupied streets of modern Rome, the city pretty blends the past and present.
Even if you’re exploring its ancient landmarks or enjoying an espresso in a cozy piazza, you can feel the timeless spirit of Rome. That’s why it truly deserves the title of the Eternal City!
Must-Know Rome Facts for Travelers

-
What is the official language spoken in Rome?
Italian is the official language, but English is widely understood in tourist areas. -
Which currency is used in Rome?
Rome uses the Euro (€) as its official currency. -
What is the best time of year to visit Rome for pleasant weather?
Spring (April to June) and fall (September to October) offer the best weather with fewer crowds. -
What is the name of the smallest country located entirely within Rome?
Vatican City is the smallest independent country in the world, located within Rome. -
Do you need a visa to visit Rome?
It depends on your nationality—EU citizens don’t need a visa, while others may require a Schengen visa. -
What is the main airport in Rome?
Leonardo da Vinci International Airport (Fiumicino) is the primary international airport. -
Is Rome a walkable city?
Yes, many of Rome’s main attractions are within walking distance, but some areas have cobblestone streets. -
What is the most famous ancient landmark in Rome?
The Colosseum, an iconic Roman amphitheater, is the most famous ancient landmark. -
What should you wear when visiting religious sites in Rome?
Modest clothing covering shoulders and knees is required in places like St. Peter’s Basilica. -
Is tap water safe to drink in Rome?
Yes, Rome’s tap water is safe, and free drinking fountains called “nasoni” are found throughout the city. -
Which public transport options are available in Rome?
Rome has buses, trams, metro lines, and taxis for getting around. -
What is Rome’s metro system like?
Rome’s metro has three lines (A, B, and C), but it’s not as extensive as other European cities. -
Do restaurants in Rome include a service charge in the bill?
Some do, but tipping is not mandatory—rounding up the bill or leaving a small tip is appreciated. -
What is the traditional Roman pasta dish made with eggs, cheese, and pancetta?
Carbonara is a classic Roman pasta dish made with those ingredients. -
Which famous landmark is home to Michelangelo’s frescoes?
The Sistine Chapel in Vatican City features Michelangelo’s renowned ceiling frescoes. -
Is there an entrance fee for the Pantheon?
Yes, as of 2023, the Pantheon charges an entrance fee, though EU residents under 18 and certain others can enter for free. -
What is the best way to skip long lines at Rome’s top attractions?
Booking skip-the-line tickets or guided tours in advance can save you hours of waiting. -
Where can you toss a coin to ensure a return trip to Rome?
The Trevi Fountain—legend says throwing a coin with your right hand over your left shoulder guarantees a return. -
What is the typical breakfast in Rome?
Italians usually have a cappuccino and a cornetto (a sweet pastry) for breakfast. -
Is Uber available in Rome?
Uber operates in Rome but mainly offers high-end services like Uber Black; taxis are more common. -
What is Rome’s main train station?
Roma Termini is the largest train station and a key transport hub in the city. -
What is the speed limit in Rome’s city center?
It’s generally 50 km/h (31 mph), but in some historic areas, it can be lower. -
Can you visit the Vatican Museums at night?
Yes, on select evenings during certain months, the Vatican Museums offer night tours. -
Which neighborhood is famous for its nightlife and local restaurants?
Trastevere is known for its lively nightlife and genuine Roman cuisine. -
What is a must-try Roman street food?
Supplì, a fried rice ball filled with tomato sauce and mozzarella, is a local favorite. -
Which Roman landmark is known for its “Mouth of Truth”?
The Bocca della Verità is an ancient marble mask that supposedly bites liars’ hands. -
What time do most restaurants in Rome serve dinner?
Dinner is typically served between 7:30 PM and 10:30 PM. -
Are credit cards widely accepted in Rome?
Yes, but small shops and cafes may prefer cash, so it’s good to carry some euros. -
Where can you see the best panoramic view of Rome?
Gianicolo Hill and the Pincian Terrace offer charming views of the city. -
What is the Roman forum, and why is it important?
The Roman Forum was the center of political, social, and commercial life in ancient Rome. -
Can you drink alcohol in public in Rome?
Yes, but there are restrictions in certain areas at night, especially near historic sites. -
What is the local law regarding crossing the street in Rome?
Pedestrians have the right of way at crosswalks, but always make eye contact with drivers before crossing! -
What is the name of the famous staircase in Rome?
The Spanish Steps, a pretty stairway connecting Piazza di Spagna to Trinità dei Monti church. -
How many fountains are in Rome?
Rome has over 1,500 fountains, more than any other city in the world! -
Where can you find ancient Roman catacombs?
The Catacombs of San Sebastiano and San Callisto are famous underground burial sites. -
Why are Roman pizzas different from Neapolitan pizzas?
Roman pizza has a thin, crispy crust, while Neapolitan pizza is softer and thicker. -
What is the historic road that connects Rome to the south of Italy?
The Appian Way (Via Appia) is one of the oldest and most important Roman roads. -
Can tourists climb the dome of St. Peter’s Basilica?
Yes, you can climb 551 steps (or take an elevator partway) for breathtaking views of Rome. -
Which famous Roman piazza is known for its fountains and street artists?
Piazza Navona, home to the Fountain of the Four Rivers and a lively atmosphere. -
What is the best way to experience Rome like a local?
Walk around, enjoy aperitivo in the evening, and avoid eating at touristy restaurants near major landmarks!
Ancient Rome Facts that Changed History
-
Who was the first emperor of Rome?
Augustus (formerly Octavian) became Rome’s first emperor in 27 BCE, marking the start of the Roman Empire. -
What was the main language spoken in Ancient Rome?
Latin was the primary language, though Greek was also widely used in the eastern provinces. -
What event led to the fall of the Western Roman Empire?
The empire fell in 476 CE when the Germanic leader Odoacer deposed the last emperor, Romulus Augustulus. -
Which Roman structure is considered one of the greatest engineering feats of the ancient world?
The aqueducts, which transported fresh water over long distances, were a groundbreaking innovation. -
What was the significance of the Roman Forum?
It was the heart of Roman political, social, and religious life, hosting speeches, trials, and markets. -
What was the purpose of the Colosseum in Ancient Rome?
It was an amphitheater used for gladiator fights, public spectacles, and dramatic performances. -
Who assassinated Julius Caesar, and why?
A group of senators, including Brutus and Cassius, assassinated him in 44 BCE to prevent him from becoming a dictator. -
What type of government did Rome have before becoming an empire?
Rome was a republic with elected officials, including consuls and senators, before transitioning to imperial rule. -
What famous road connected Rome to its far-reaching territories?
The Appian Way (Via Appia) was one of the first major Roman roads, crucial for military and trade routes. -
What was the name of the elite Roman soldiers who protected the emperor?
The Praetorian Guard served as the emperor’s personal bodyguards and elite troops. -
Which volcanic eruption in 79 CE buried the cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum?
Mount Vesuvius erupted, preserving the cities under layers of ash and pumice. -
What were Roman gladiators?
Gladiators were trained fighters, often slaves or prisoners, who battled in arenas for public entertainment. -
What was the Pantheon originally built for?
It was a temple dedicated to all Roman gods and later converted into a Christian church. -
What was the Roman Senate?
It was the governing body of the Roman Republic, composed of aristocrats who influenced laws and policies. -
How did Roman concrete contribute to construction ?
Roman concrete (opus caementicium) was extremely durable, enabling the construction of massive structures like the Colosseum and aqueducts. -
What was the Pax Romana?
A 200-year period of relative peace and stability across the Roman Empire, starting with Augustus. -
Which emperor split the Roman Empire into Eastern and Western halves?
Emperor Diocletian divided the empire in 285 CE to improve governance. -
What was the Circus Maximus used for?
It was a massive stadium in Rome used for chariot races and other public spectacles. -
Who were the plebeians and patricians in Roman society?
Plebeians were commoners, while patricians were the aristocratic elite. -
What was the purpose of Roman baths?
They served as social hubs where Romans bathed, exercised, and conducted business. -
Who was Spartacus, and what did he do?
Spartacus was a gladiator who led a massive slave rebellion against Rome in 73–71 BCE. -
How did Rome’s military help expand its empire?
Rome’s disciplined legions, advanced tactics, and engineering skills helped it conquer vast territories. -
What is the significance of the Twelve Tables?
The Twelve Tables were Rome’s first written legal code, forming the foundation of Roman law. -
Which Roman emperor converted to Christianity and legalized the religion?
Constantine the Great converted to Christianity and issued the Edict of Milan in 313 CE, granting religious freedom. -
What was the function of Roman insulae?
Insulae were multi-story apartment buildings where most urban Romans lived. -
Which Roman invention revolutionized public sanitation?
The sewer system, particularly the Cloaca Maxima, helped manage waste and improve hygiene. -
What was a triumph in Ancient Rome?
A triumph was a grand parade celebrating a victorious general’s success in battle. -
Which emperor built a massive defensive wall in Britain?
Emperor Hadrian built Hadrian’s Wall to protect Roman Britain from northern tribes. -
What role did the Roman gods play in daily life?
Romans believed the gods influenced all aspects of life, from politics to household affairs, and worshipped them through rituals. -
What was the name of the standard currency in Ancient Rome?
The denarius was the most widely used silver coin in Rome. -
How did Roman roads impact the empire?
The vast road network allowed efficient military movement, trade, and communication across the empire. -
Which Roman building still has the world’s largest unreinforced concrete dome?
The Pantheon’s dome remains a marvel of ancient engineering. -
What was the name of the largest Roman amphitheater ever built?
The Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheater, remains the largest. -
Which Roman leader famously crossed the Rubicon, starting a civil war?
Julius Caesar crossed the Rubicon River in 49 BCE, defying the Senate and leading to civil war. -
What role did slaves play in Ancient Rome?
Slaves were essential to Roman society, working in households, farms, and public projects. -
Who were the Vestal Virgins?
They were priestesses who maintained the sacred fire of Vesta and took a vow of chastity. -
Which Roman emperor supposedly “fiddled while Rome burned”?
Nero was blamed for the Great Fire of Rome in 64 CE, though it’s debated Even if he was responsible. -
What was the Roman amphitheater in modern-day France called?
The Arena of Nîmes is one of the best-preserved Roman amphitheaters. -
Which Roman general defeated Hannibal in the Second Punic War?
Scipio Africanus defeated Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BCE. -
What was the ultimate legacy of Ancient Rome?
Rome’s contributions to law, engineering, construction , language, and governance continue to shape modern civilization.
Modern Rome Facts that Will Surprise You

-
Who founded the city of Rome, according to legend?
According to legend, Rome was founded by the twin brothers Romulus and Remus in 753 BCE. -
What was the name of the first set of Roman laws written for public display?
The Twelve Tables, established around 450 BCE, were the first written laws of Rome. -
How did Ancient Rome influence modern democracy?
Rome’s republican system, with elected officials and checks on power, influenced modern democratic governments. -
What were the Punic Wars, and why were they significant?
The Punic Wars (264–146 BCE) were a series of conflicts between Rome and Carthage, leading to Rome’s dominance in the Mediterranean. -
Who was Hannibal, and why is he famous in Roman history?
Hannibal was a Carthaginian general who led a daring invasion of Italy, famously crossing the Alps with war elephants. -
What was the role of the Roman dictator?
A dictator was given temporary absolute power during emergencies, typically for six months. -
Which emperor built the Colosseum?
Emperor Vespasian started construction, and his son Titus completed it in 80 CE. -
What was the primary purpose of the Roman census?
The census helped determine taxation, military service obligations, and social status. -
What was the role of a consul in the Roman Republic?
Two consuls were elected annually to lead the government and military. -
How did Julius Caesar change the Roman Republic?
His rise to power, military conquests, and eventual assassination marked the end of the Republic and the rise of the Empire. -
Which battle marked the end of the Roman Republic?
The Battle of Actium in 31 BCE, where Octavian defeated Mark Antony and Cleopatra, led to the start of the Roman Empire. -
Who were the equites in Roman society?
The equites were a social class of wealthy merchants and landowners, ranking below the senatorial class. -
What was the main purpose of Roman aqueducts?
They transported fresh water to cities, public baths, and fountains. -
What did Romans use as a form of central heating?
The hypocaust system used underground fires to heat homes and baths. -
Which Roman leader was given the title “Princeps” instead of “King” or “Emperor”?
Augustus preferred the title “Princeps,” meaning “First Citizen,” to avoid the perception of tyranny. -
Which emperor built the massive baths of Rome that still bear his name?
Emperor Caracalla built the Baths of Caracalla, one of the largest bathing complexes in Rome. -
What was a Roman triumphal arch used for?
Triumphal arches commemorated military victories and honored emperors or generals. -
Which Roman emperor is credited with building a vast network of roads?
Augustus expanded and improved the Roman road system, famously summarized as “All roads lead to Rome.” -
What was the significance of the Edict of Milan in 313 CE?
It granted religious tolerance to Christians, ending their persecution in the Roman Empire. -
Who was the last emperor of the Western Roman Empire?
Romulus Augustulus was the last emperor, deposed in 476 CE by the Germanic leader Odoacer. -
What was the name of Rome’s first emperor’s adopted father?
Julius Caesar adopted Octavian (Augustus), paving the way for his rise to power. -
What was the official title of the rulers of the Eastern Roman Empire?
They were called Byzantine Emperors after the empire split into East and West. -
What was the role of the Roman Vestal Virgins?
They were priestesses responsible for maintaining the sacred fire of Vesta and had great social privileges. -
What did Roman soldiers receive as payment?
Roman soldiers were paid in denarii and sometimes given land upon retirement. -
Which Roman province was the farthest north?
Britannia, including parts of modern England, Scotland, and Wales, was Rome’s northernmost province. -
Who wrote “The Aeneid,” Rome’s great massive poem?
The poet Virgil wrote The Aeneid, a mythological story about Rome’s founding. -
What was a Roman legion?
A legion was the primary military unit of Rome, consisting of about 4,800 to 6,000 soldiers. -
What was the most common form of Roman entertainment?
Gladiator battles, chariot races, theater performances, and public feasts were popular forms of entertainment. -
How did Rome expand its empire so successfully?
Rome combined military conquest, strategic alliances, engineering skills, and integration of conquered peoples into its system. -
Which Roman philosopher was also a statesman and orator?
Cicero was a famous Roman statesman, philosopher, and orator known for his writings and speeches. -
Which emperor declared himself a god while still alive?
Emperor Caligula declared himself a living god and demanded worship. -
What was the significance of the Julian calendar?
Introduced by Julius Caesar in 45 BCE, it became the basis for the modern Gregorian calendar. -
Which Roman emperor supposedly built a golden palace after the Great Fire of Rome?
Nero built the Domus Aurea, a lavish palace, after the fire of 64 CE. -
What was the name of Rome’s most powerful governing body during the Republic?
The Senate held the most political influence and power in the Republic. -
Which Roman temple is considered one of the best-preserved ancient buildings?
The Pantheon, with its massive dome, is one of the best-preserved structures from Ancient Rome. -
How did Roman citizenship benefit individuals?
Citizens had legal rights, protection under Roman law, and access to public services. -
What caused the Third Servile War, famously led by Spartacus?
It was a massive slave uprising against Roman rule, led by the gladiator Spartacus in 73–71 BCE. -
Which emperor built a massive forum bearing his name?
Emperor Trajan built Trajan’s Forum, a vast complex of markets and public spaces. -
What was a Roman basilica originally used for?
Basilicas were public buildings used for legal and business matters, later inspiring Christian church construction . -
What was the long-term impact of Ancient Rome on Western civilization?
Rome’s legacy includes law, language (Latin-based Romance languages), construction , engineering, governance, and philosophy.
Fun and Weird Rome Facts to Astonish You

-
Which tiny country is located entirely inside Rome?
Vatican City is the world’s smallest country, completely surrounded by Rome. -
What unusual type of gladiator once fought in the Colosseum?
Some gladiators fought using only a net and a trident, known as Retiarius. -
What is the meaning of the saying “All roads lead to Rome”?
It comes from the Roman road network, where all major roads extended from the capital. -
Why does Rome have so many cats?
Cats are protected by law and roam freely, especially in ruins like Largo di Torre Argentina. -
What unique tradition involves the Trevi Fountain?
Tossing a coin over your shoulder into the fountain is said to guarantee a return to Rome. -
What unusual law existed in Ancient Rome about wearing purple?
Only emperors could wear purple togas, as the dye was rare and expensive. -
Which famous artist designed St. Peter’s Basilica’s dome?
Michelangelo designed the massive dome, though he didn’t live to see it completed. -
What bizarre thing did Emperor Caligula do with his horse?
He reportedly tried to make his horse, Incitatus, a consul (a high-ranking official). -
How many steps are in the Spanish Steps?
There are 135 steps connecting Piazza di Spagna to the Trinità dei Monti church. -
What did Romans use instead of toilet paper?
They used a spongia, a communal sponge on a stick, cleaned with vinegar. -
What strange event happens at the Pantheon every year?
On Pentecost Sunday, thousands of rose petals are dropped through the oculus. -
What was the Roman vomitorium, and was it used for vomiting?
Despite myths, vomitoria were actually exit passages in amphitheaters, not rooms for vomiting. -
What is the nickname of Rome due to its location?
It’s called the “City of Seven Hills” because it was built on seven hills. -
What do Romans call their city in Latin?
In Latin, Rome is called Roma, which is still its Italian name today. -
What is unique about the Mouth of Truth (Bocca della Verità)?
Legend says it bites the hand of liars who place their hand inside its mouth. -
Which Roman fountain collects the most coins daily?
The Trevi Fountain collects around €3,000 daily, donated to charity. -
Which church in Rome is made entirely of human bones?
The Capuchin Crypt is decorated with the bones of thousands of Capuchin monks. -
Why do some buildings in Rome have no doors?
Ancient temples, like the Pantheon, have enormous entrances with no doors. -
What unusual animals once lived in the Colosseum?
Exotic animals like lions, elephants, and even hippos were used in fights. -
What’s special about Rome’s Piazza Navona?
It was built on the site of an ancient Roman stadium, and its shape still reflects the old track. -
How old is the world’s first shopping mall, built in Rome?
Trajan’s Market, built in the 2nd century CE, is considered the first shopping mall. -
What strange material did Romans use for makeup?
Roman women used lead-based makeup, which was highly toxic. -
What is the longest-operating restaurant in Rome?
La Campana, established in 1518, is considered Rome’s oldest continuously operating restaurant. -
What is the significance of the “Talking Statues” of Rome?
Romans used them to post anonymous political messages in the 16th century, a tradition that continues today. -
What Roman emperor was so paranoid that he banned mirrors?
Emperor Domitian reportedly banned mirrors to prevent assassination plots. -
What is Rome’s oldest road still in use?
The Appian Way (Via Appia), built in 312 BCE, is still walkable today. -
What was unusual about Emperor Nero’s rotating dining room?
His Domus Aurea (Golden House) featured a rotating banquet hall powered by water mechanisms. -
Why does Rome’s Tiber Island look like a boat?
It was designed to resemble a ship as a tribute to the legend of a miraculous plague cure. -
Which church in Rome has a hidden optical illusion inside?
Sant’Ignazio Church has a painted ceiling that appears to be a real dome but is actually flat. -
How did Ancient Romans keep time without clocks?
They used sundials and large public water clocks to track time. -
What is the hidden underground city beneath Rome?
Rome has miles of catacombs, ancient underground burial sites.
Final Thoughts
Rome’s history stands as one of humanity’s most significant chapters.
Through these 151 facts, we’ve traveled across centuries of triumph, innovation, and cultural growth that continue to influence our world today.
These glimpses into ancient Roman life show how a small settlement grew into an empire that shaped laws, languages, and lifestyles across continents.
The stories of Rome remind us that history isn’t just about dates and names—it’s about people who faced challenges not unlike our own.
For those who enjoyed these Roman facts, our other guides on Taylor Swift facts, Harry Potter facts, and giraffe facts offer similarly appealing pitches to different subjects.
Each fact collection provides the same careful attention to accuracy and interesting details that make learning both fun and valuable.
History teaches us where we came from, helping us understand where we might go next.