Looking for space facts that go beyond the basics? Most people know Neptune is blue and far away.
They’ve seen the photos and memorized their place in the solar system. But there’s a whole universe of Neptune knowledge that’s absolutely mind-blowing.
People have been interested in this distant ice giant for years. And trust me, Neptune is way more interesting than most astronomy books let on.
Did you know it rains diamonds in Neptune’s atmosphere? Or that its moon Triton is slowly moving closer and will eventually be torn apart?
These 87 Neptune facts will change how you see our solar system’s most mysterious planet.
The Mystery of Neptune’s Discovery
Neptune wasn’t found by accident. It was actually predicted by math before anyone saw it! In the early 1800s, astronomers noticed Uranus wasn’t moving exactly as it should. They thought another planet’s gravity must be pulling on it.
Two mathematicians, John Couch Adams from England and Urbain Le Verrier from France, separately calculated where this mystery planet should be. Le Verrier sent his math to the Berlin Observatory.
On September 23, 1846, astronomer Johann Galle looked where Le Verrier predicted and found Neptune that very night!
This made Neptune the first planet discovered through mathematical predictions rather than regular observation. It was a huge win for science, showing how math could help us find things we can’t even see yet.
Neptune’s Secrets: Size, Composition, and What Makes It So Unique
Neptune is the fourth-largest planet in our solar system. It measures about 30,600 miles (49,244 km) across at its equator. If Earth were a baseball, Neptune would be about the size of a basketball.
As an ice giant, Neptune isn’t made of rock like Earth. It has three main layers:
- A small rocky core about the size of Earth
- A thick middle layer of water, ammonia, and methane ice
- A gassy outer layer of hydrogen, helium, and methane
The methane in Neptune’s atmosphere absorbs red light and reflects blue light. That’s why Neptune appears such a striking deep blue color in photos!
Neptune is denser than gas giants like Jupiter. Scientists believe it contains a higher percentage of heavy elements than the larger gas giants.
Interesting and Fun Facts About Neptune
- Neptune is the eighth and most distant planet in our solar system.
- It was discovered in 1846 using mathematical predictions rather than direct observation.
- Neptune is named after the Roman god of the sea.
- It is one of two ice giants in the solar system, the other being Uranus.
- Neptune’s atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen, helium, and methane.
- Methane in Neptune’s atmosphere absorbs red light and reflects blue, giving it its blue color.
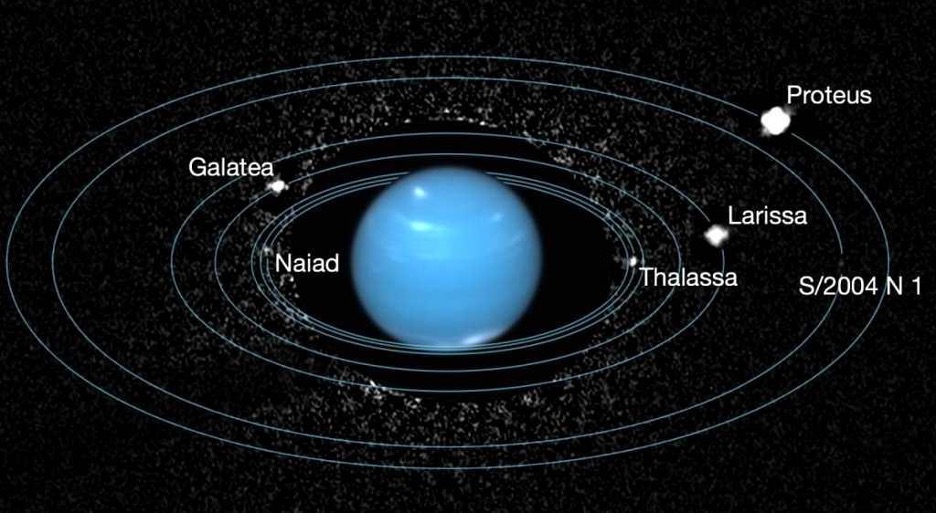
- Neptune has 16 known moons.
- Its largest moon is Triton, which was discovered just 17 days after Neptune itself.
- Triton is geologically active, with cryovolcanoes that spew nitrogen ice and dust.
- Neptune has at least five faint rings made of dust and ice particles.
- The planet’s equatorial diameter is about 49,528 kilometers (30,775 miles).
- Neptune is about four times wider than Earth.
- It is about 30 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun, roughly 4.5 billion kilometers.
- Sunlight takes about 4 hours to reach Neptune.
- Neptune completes one orbit around the Sun every 165 Earth years.
- High noon on Neptune would look like dim twilight from Earth’s perspective.
- Neptune’s atmosphere extends deeply and gradually merges into a hot, dense fluid of “icy” materials.
- Scientists believe Neptune may have an ocean of superheated water beneath its clouds.
- Neptune has the strongest winds in the solar system, reaching speeds over 2,000 kilometers per hour (1,200 mph).
- These winds are three times stronger than Jupiter’s and nine times stronger than Earth’s.
- The Great Dark Spot was a massive storm on Neptune similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.
- The Great Dark Spot was first observed by Voyager 2 in 1989 but disappeared by 1994.
- New dark spots and storms have appeared on Neptune since then.
- Neptune spins rapidly, completing a rotation in about 16 hours.
- Neptune is the densest of the giant planets.
- Its mass is 17 times that of Earth.
- Neptune is slightly smaller but more massive than Uranus.
- The planet’s gravity compresses its atmosphere, making it denser than Uranus’s.
- Neptune’s interior consists of a small rocky core surrounded by a thick mantle of water, ammonia, and methane ices.
- The core of Neptune is about the same mass as Earth.
- Neptune’s atmosphere contains thin, high clouds made of methane ice crystals.
- The planet’s blue color is slightly darker than Uranus’s.
- Neptune’s rings are faint and difficult to observe from Earth.
- The rings are composed of ice particles mixed with dust and possibly carbon-based compounds.
- Neptune was the first planet discovered by mathematical prediction rather than direct observation.
- French mathematician Urbain Le Verrier and English mathematician John Couch Adams predicted Neptune’s position.
- Johann Galle was the astronomer who first observed Neptune in 1846 based on these calculations.
- Neptune is not visible to the naked eye from Earth.
- The Voyager 2 spacecraft is the only probe to have visited Neptune, flying by in 1989.
- Voyager 2 provided the first close-up images of Neptune and its moons.
- The Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based telescopes continue to study Neptune.
- Neptune’s atmosphere is colder than Uranus’s despite being closer to the Sun.
- The planet’s temperature can drop to about -214 degrees Celsius (-353 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Neptune’s axial tilt is about 28.3 degrees, similar to Earth’s tilt.
- This tilt causes seasonal changes on Neptune, but each season lasts over 40 Earth years.
- Neptune’s magnetic field is tilted about 47 degrees from its rotational axis.
- The magnetic field is offset from the planet’s center by about 0.55 radii.
- Neptune’s magnetic field is about 27 times more powerful than Earth’s.
- The planet’s atmosphere has visible cloud features that change rapidly.
- Neptune’s clouds include dark spots, bright clouds, and streaks.
- The planet’s weather is powered internally rather than by sunlight.
- Neptune emits more energy than it receives from the Sun.
- The internal heat drives the planet’s extreme winds and storms.
- Neptune’s orbit is nearly circular but slightly elliptical.
- The planet’s average orbital speed is about 5.43 km/s (3.37 miles/s).
- Neptune’s rotation causes an equatorial bulge, making it slightly oblate.
- The planet’s apparent magnitude varies between 7.67 and 8.00, making it only visible with telescopes.
- Neptune’s angular diameter as seen from Earth ranges from 2.2 to 2.4 arcseconds.
- The planet’s albedo (reflectivity) is about 0.29 (Bond albedo).
- Neptune’s atmosphere has a scale height of about 19.7 km.
- Neptune’s atmosphere contains trace amounts of hydrocarbons and possibly hydrogen sulfide.
- The planet’s atmosphere is layered, with a troposphere, stratosphere, and thermosphere.
- Neptune’s troposphere contains clouds of methane ice.
- The planet’s stratosphere is heated by solar ultraviolet light.
- Neptune’s thermosphere is very hot due to solar radiation and charged particle interactions.
- Neptune’s rings have arcs—clumps of dust and rock particles that are gravitationally confined.
- The arcs are named Liberté, Egalité, Fraternité, Courage, and Adélie.
- Triton’s orbit around Neptune is retrograde, meaning it moves opposite Neptune’s rotation.
- Triton is one of the coldest objects in the solar system, with surface temperatures near -235 degrees Celsius.
- Triton’s surface is mostly frozen nitrogen with some methane and carbon monoxide ices.
- Triton’s geysers eject nitrogen gas and dust into space.
- Triton is believed to be a captured Kuiper Belt object.
- Neptune’s other moons are much smaller and irregularly shaped.
- Neptune’s moons include Proteus, Nereid, Larissa, Galatea, and Despina.
- Neptune’s gravitational influence affects the orbits of nearby Kuiper Belt objects.
- Neptune’s discovery confirmed the existence of unseen planets affecting Uranus’s orbit.
- The planet’s name and symbol reflect its association with the sea and water.
- Neptune’s discovery was a major triumph for celestial mechanics and mathematics.
- The planet’s discovery led to improvements in orbital calculations and predictions.
- Neptune’s atmosphere contains clouds that can form and dissipate in days or weeks.
- The planet’s weather patterns are complex and not fully understood.
- Neptune’s magnetic field likely originates from a conductive fluid layer inside the planet.
- The planet’s interior heat source is not fully explained but may involve slow gravitational contraction.
- Neptune’s orbit takes it about 4.5 billion kilometers from the Sun on average.
- Because of its distance, Neptune’s sunlight is about 900 times weaker than Earth’s.
- Neptune’s atmosphere is too harsh and cold to support life as we know it.
- Future missions to Neptune are planned, but none have launched yet.
Neptune’s Cosmic Dance: Orbit, Rotation, and What It All Means

Neptune moves in its own special way through space. Let’s explore how this far blue planet spins and circles the Sun!
Neptune’s Super Long Year
Neptune takes a really long time to go around the Sun – 165 Earth years for just one Neptune year! This means if you were born on Neptune, you wouldn’t have your first birthday until you were older than any human has ever lived.
Why does it take so long? Neptune sits very far from the Sun – about 2.8 billion miles away. That’s 30 times farther than Earth! Sunlight takes 4 hours to reach Neptune, but only 8 minutes to reach us.
Neptune’s path around the Sun is almost a perfect circle, which is different from most planets that have more oval-shaped paths.
Neptune’s Quick Day
Even though Neptune’s year is super long, its day is pretty short. The planet spins once every 16 Earth hours. That’s faster than our 24-hour day, even though Neptune is much bigger than Earth!
This fast spinning makes Neptune bulge a little at its middle. It’s about 3% wider at its equator than from top to bottom.
Scientists learned how fast Neptune spins by watching clouds move around in its atmosphere.
Seasons on Neptune
Like Earth, Neptune tilts to one side as it spins, about 28 degrees (Earth tilts at 23.5 degrees). This tilt gives Neptune seasons, just like we have.
But Neptune’s seasons last about 40 Earth years each! Summer would last four decades! Since people first discovered Neptune in 1846, we haven’t even seen it go through all four seasons yet.
Sometimes Farther Than Pluto
Here’s something cool – from 1979 to 1999, Neptune was actually farther from the Sun than Pluto. This happened because Pluto’s path sometimes brings it closer to the Sun than Neptune.
This won’t happen again until 2227, so right now Neptune is the most distant planet in our solar system.
The Bottom Line
Neptune remains one of our solar system’s most fascinating planets. From its mysterious discovery through mathematical predictions to its extreme weather patterns and unique moons, this blue giant continues to surprise scientists with each new observation.
These 87 facts highlight just how special Neptune truly is in our cosmic neighborhood. Its diamond rain, powerful winds, and backwards-orbiting moon Triton all remind us how diverse planetary conditions can be.
As technology advances, we’ll undoubtedly find out even more secrets about this distant world.
Until then, looking up at the night sky, remember that this tiny blue dot holds wonders we’re still working to understand.