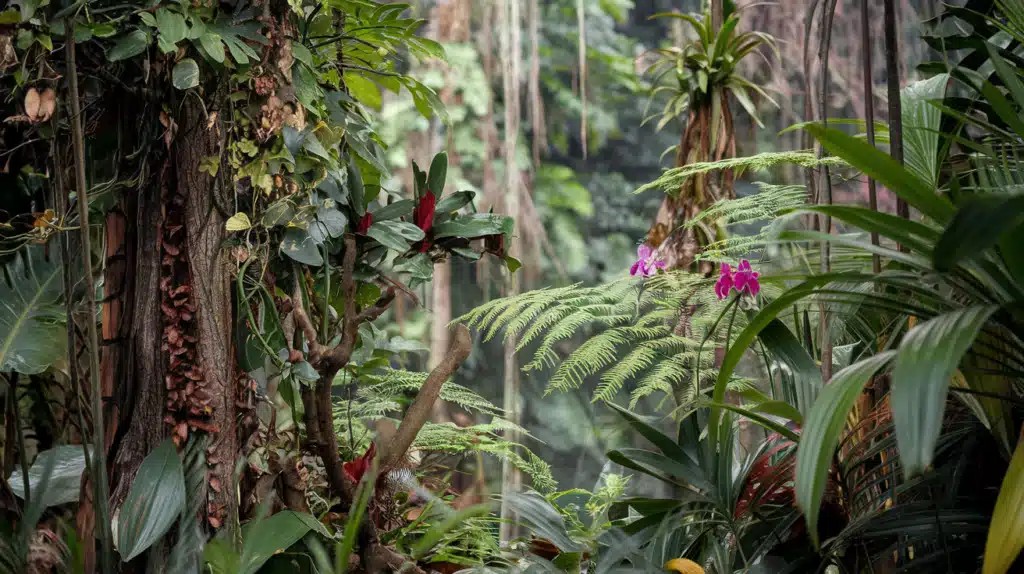
Imagine standing in Earth’s most amazing garden.
When visitors first step into a tropical rainforest, they are struck by the sheer number of layers of green life stretching as far as the eye can see.
But here’s the thing: these plants aren’t just pretty greenery.
A biologist once found that a single rainforest plant could hold the key to treating certain illnesses, showing how these forests are more than just natural wonders.
From tiny orchids hiding in the shadows to towering giants that touch the clouds, tropical rainforest plants tell incredible stories of survival, adaptation, and pure natural genius.
Key Characteristics of Tropical Rainforest Plants
-
Large, Broad Leaves- Designed to capture maximum sunlight in the shaded understory.
-
Drip Tips- Pointed leaf tips allow excess rainwater to run off, preventing mold and bacteria growth.
-
Epiphytic Growth- Many plants, like orchids and bromeliads, grow on trees to reach sunlight without rooting in the ground.
-
Buttress Roots- Wide, shallow roots support tall trees in the thin rainforest soil.
-
Rapid Growth- Plants grow quickly to compete for limited sunlight in the dense canopy.
-
Evergreen Nature- Most plants keep their leaves year-round due to the constant warm and wet climate.
-
Climbing Vines (Lianas)- Vines climb tree trunks to access sunlight in the upper canopy.
-
Thin Bark- With no need for protection against cold, many rainforest trees have smooth, thin bark.
-
Toxicity and Defense Mechanisms- Some plants produce toxins, thorns, or tough leaves to deter herbivores.
-
Shade Tolerance- Understory plants adapt to low light conditions with large, dark green leaves for efficient photosynthesis.
-
Water Storage Capabilities- Some plants, such as bromeliads, store water in their leaves, supporting small ecosystems.
Interesting Plants Found in Tropical Rainforest
1. Kapok Tree
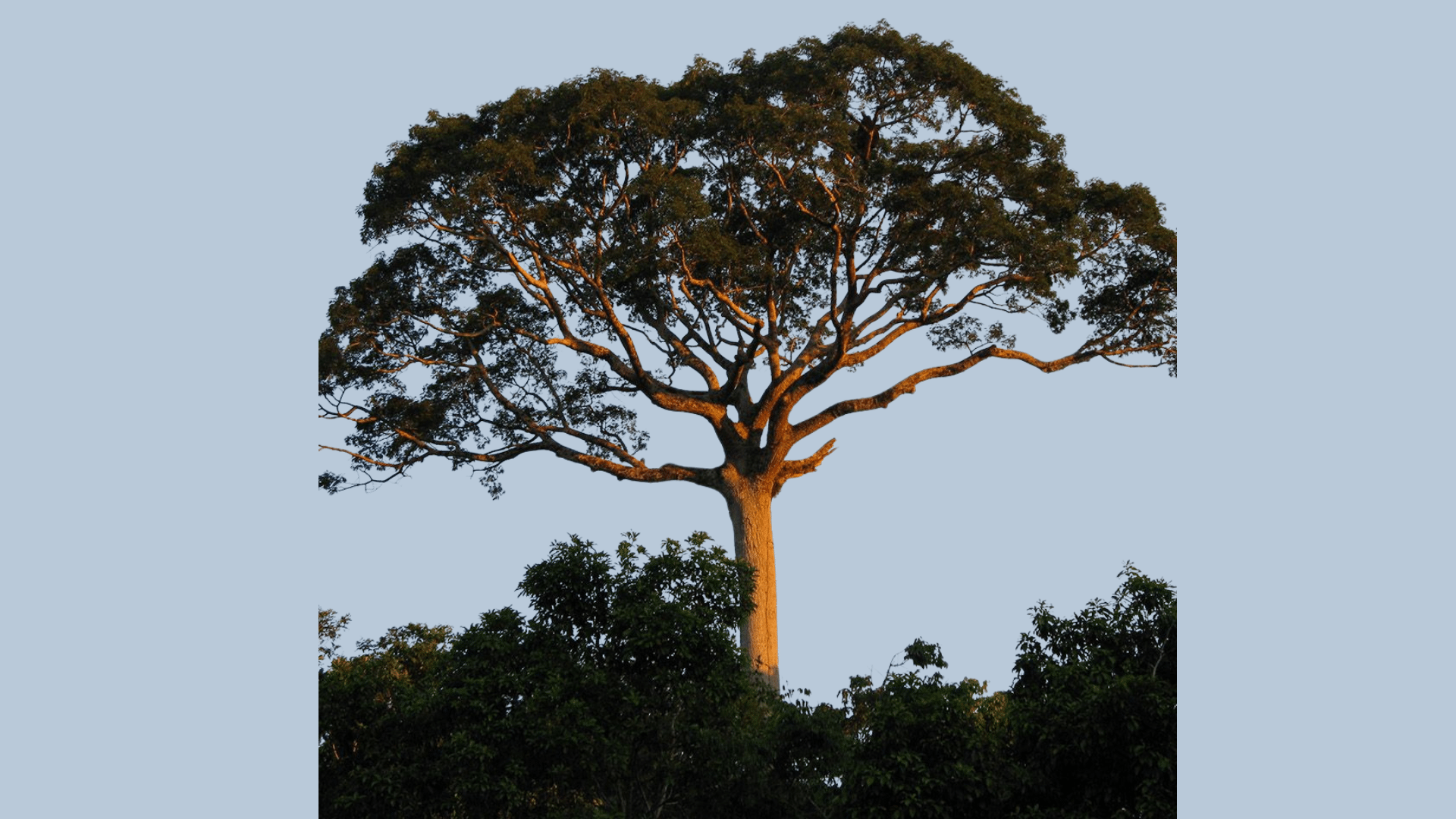

- Interesting Fact: Grows up to 200 feet tall, with massive buttress roots.
- Cultural Significance: Sacred in Mayan mythology, representing the connection between the underworld, earth, and sky.
- Growth Habits: Fast-growing canopy tree.
- Uses by Humans: Fibers are used for pillows and life jackets, and wood is used for carving.
2. Rubber Tree

- Interesting Facts: Main source of natural rubber.
- Cultural Significance: Crucial in the Industrial Revolution for tires and machinery.
- Growth Habits: Medium to large tree with latex-producing bark.
- Uses by Humans: Latex harvested for rubber products.
3. Strangler Fig
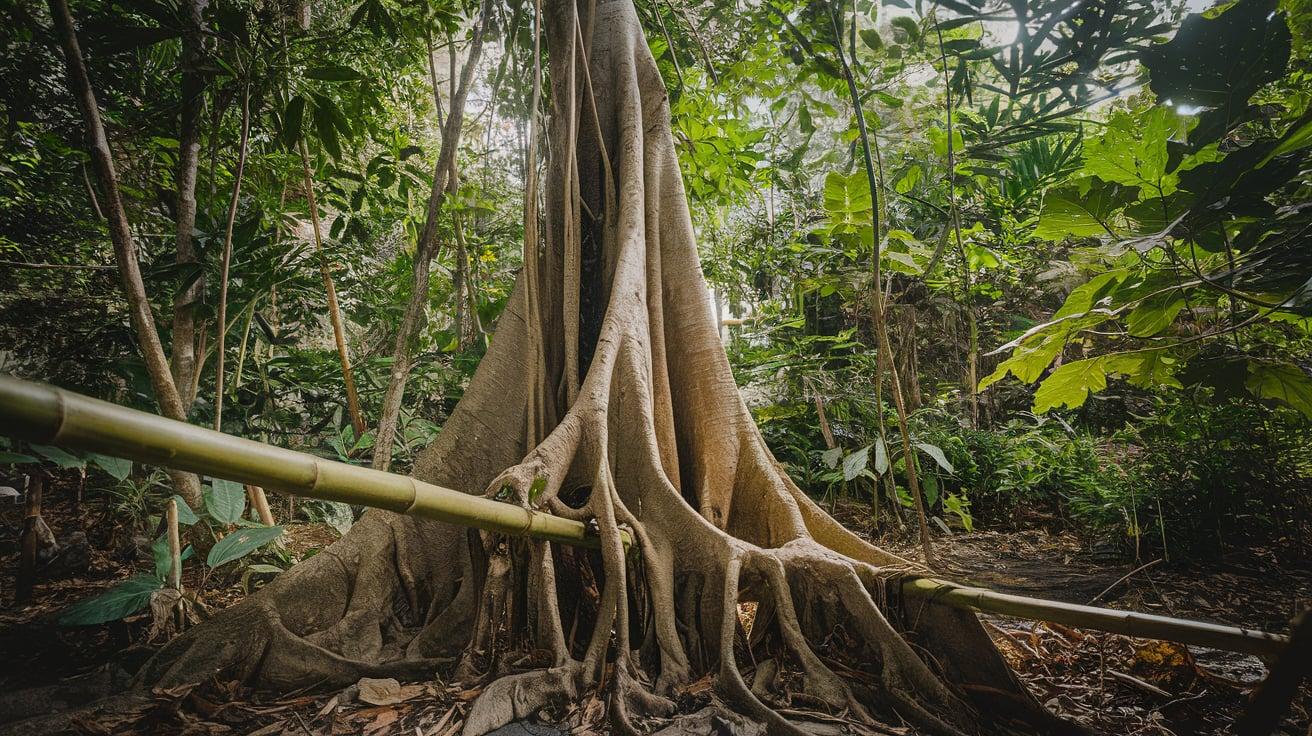

- Interesting Facts: It starts as an epiphyte and strangles host trees.
- Cultural Significance: Considered sacred in various Asian cultures.
- Growth Habits: Grows around host trees, eventually becoming freestanding.
- Uses by Humans: Fruit feeds wildlife; wood is used locally.
4. Bromeliads
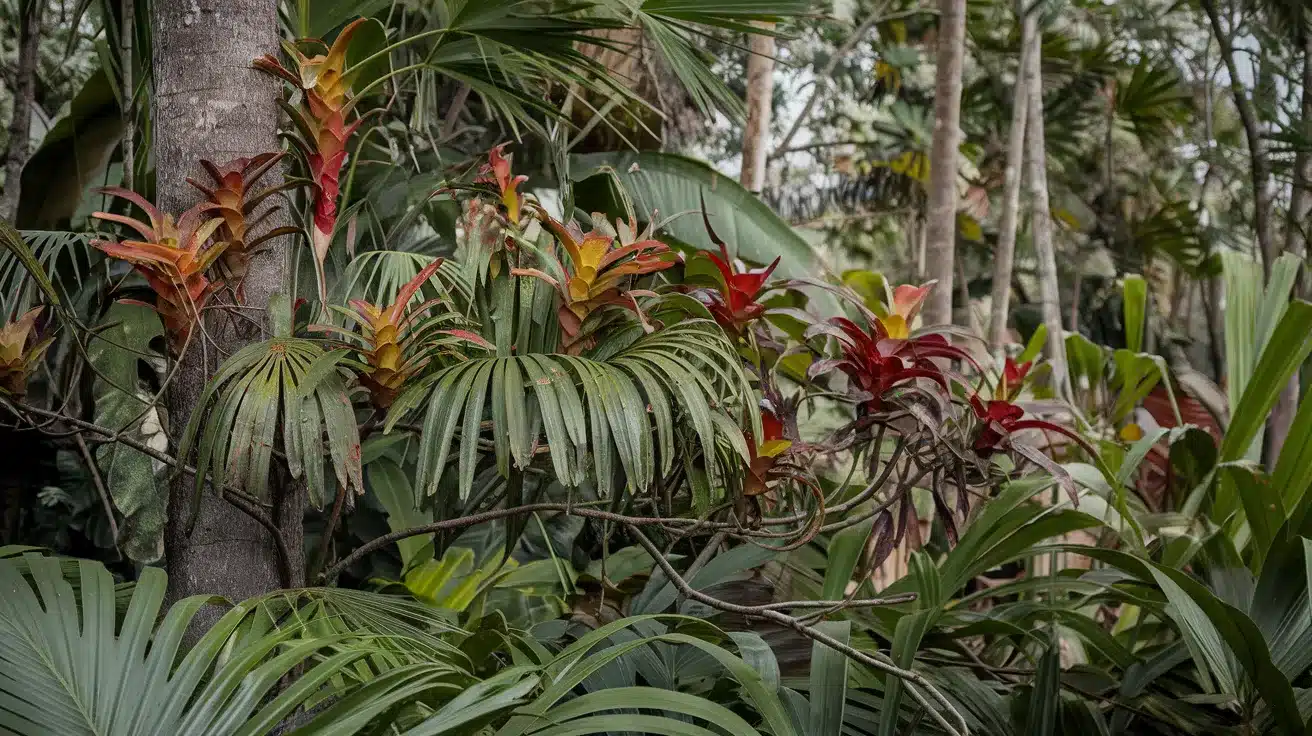

- Interesting Facts: Leaves hold water, forming mini-ecosystems.
- Cultural Significance: Symbolize resilience in some cultures.
- Growth Habits: Grow on trees (epiphytic) or the ground.
- Uses by Humans: Ornamental plants; some species edible.
5. Orchids
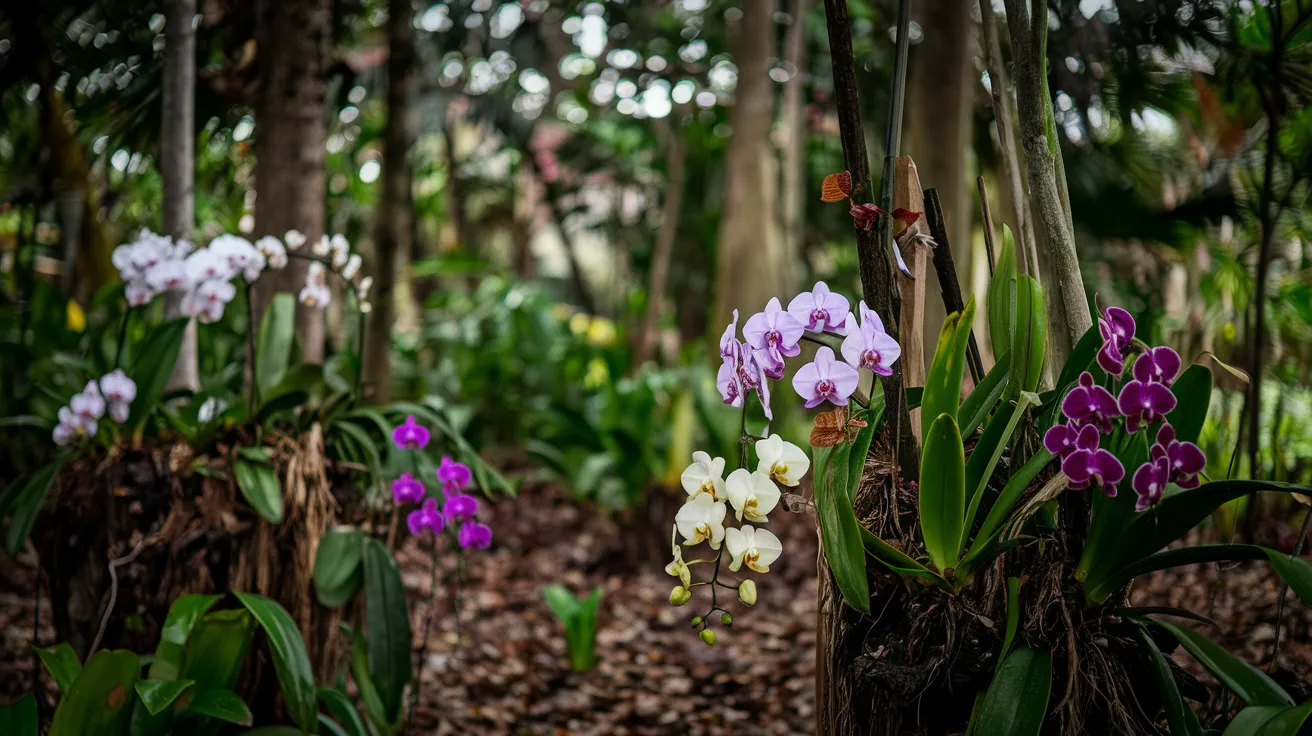

- Interesting Facts: One of the largest plant families.
- Cultural Significance: Symbol of love and beauty worldwide.
- Growth Habits: Mostly epiphytic, growing on trees.
- Uses by Humans: Ornamental and used in perfumes.
6. Heliconia
![]()
- Interesting Facts: Known as “lobster claws” for vibrant bracts.
- Cultural Significance: Featured in tropical floral arrangements.
- Growth Habits: Herbaceous plants with large leaves.
- Uses by Humans: Ornamental purposes in landscaping.
7. Passionflower
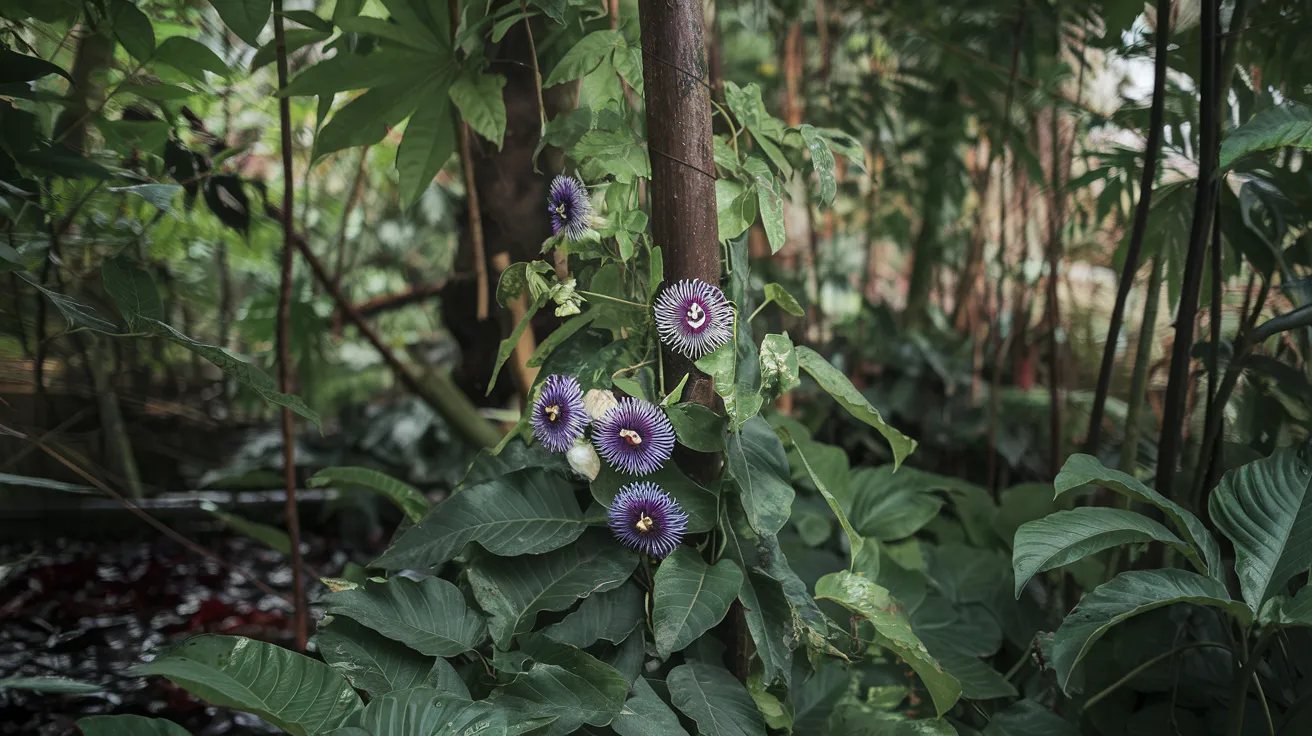

- Interesting Facts: Unique flower structure with edible fruit.
- Cultural Significance: Symbolizes passion in Christian traditions.
- Growth Habits: Climbing vines with tendrils.
- Uses by Humans: Fruit is used for juices and herbal remedies.
8. Banana Plant
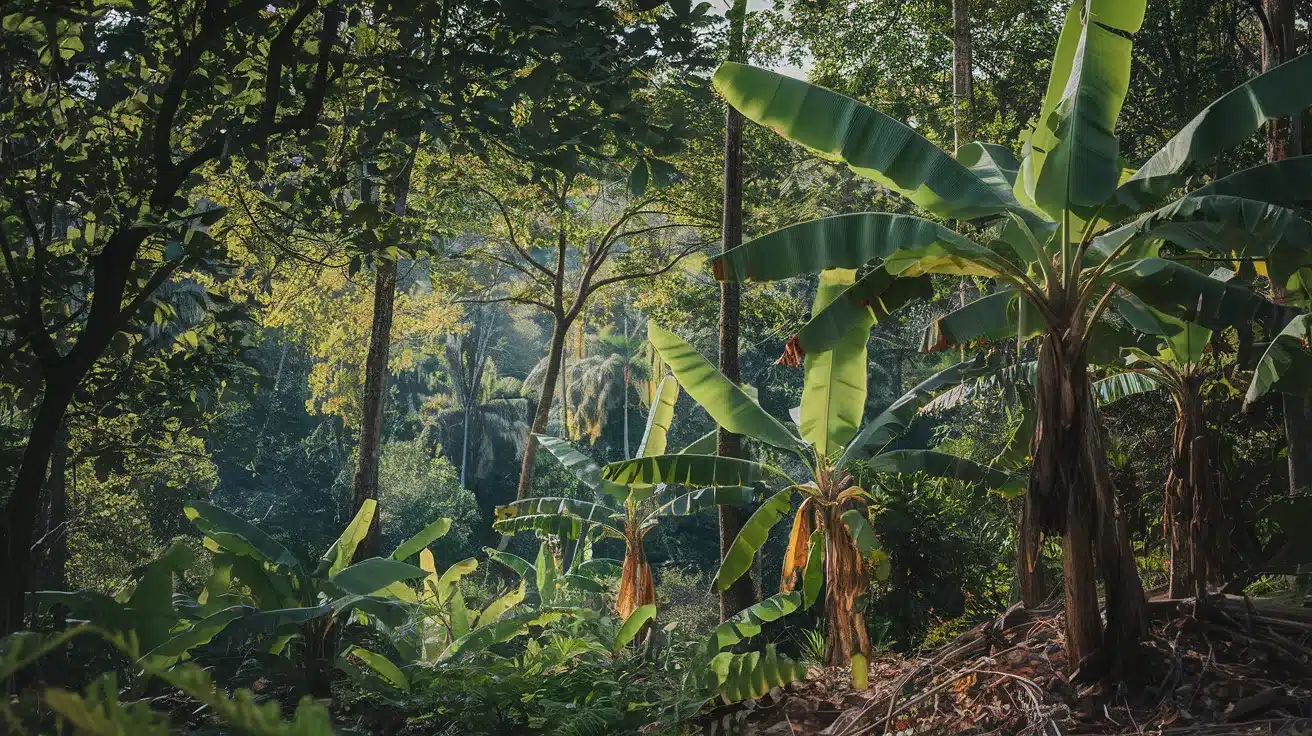

- Interesting Facts: Technically, it’s a giant herb, not a tree.
- Cultural Significance: Staple food in many tropical cultures.
- Growth Habits: Rapid growth with large leaves.
- Uses by Humans: Fruit for consumption; leaves for cooking.
9. Cacao Tree
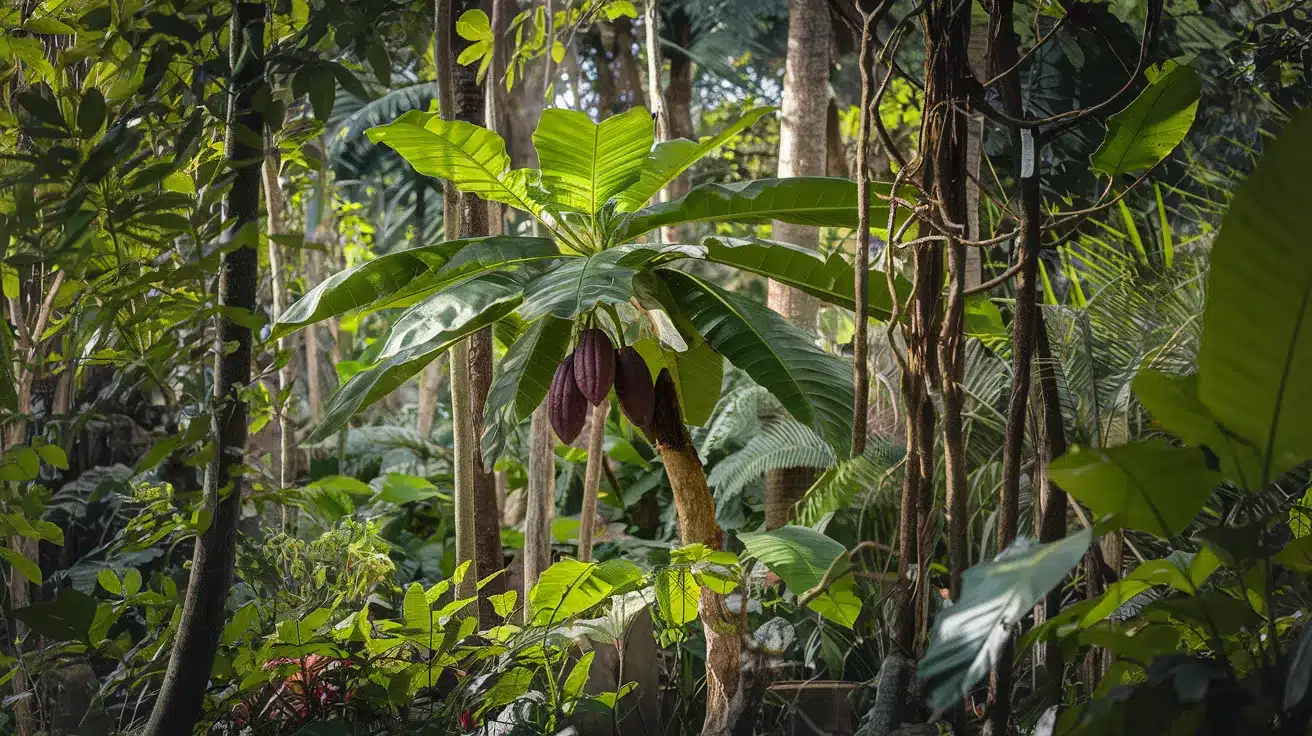

- Interesting Facts: Produces cocoa beans for chocolate.
- Cultural Significance: Sacred to ancient Mesoamerican civilizations.
- Growth Habits: Small understory tree.
- Uses by Humans: Beans are used in chocolate and cosmetics.
10. Rattan Palm
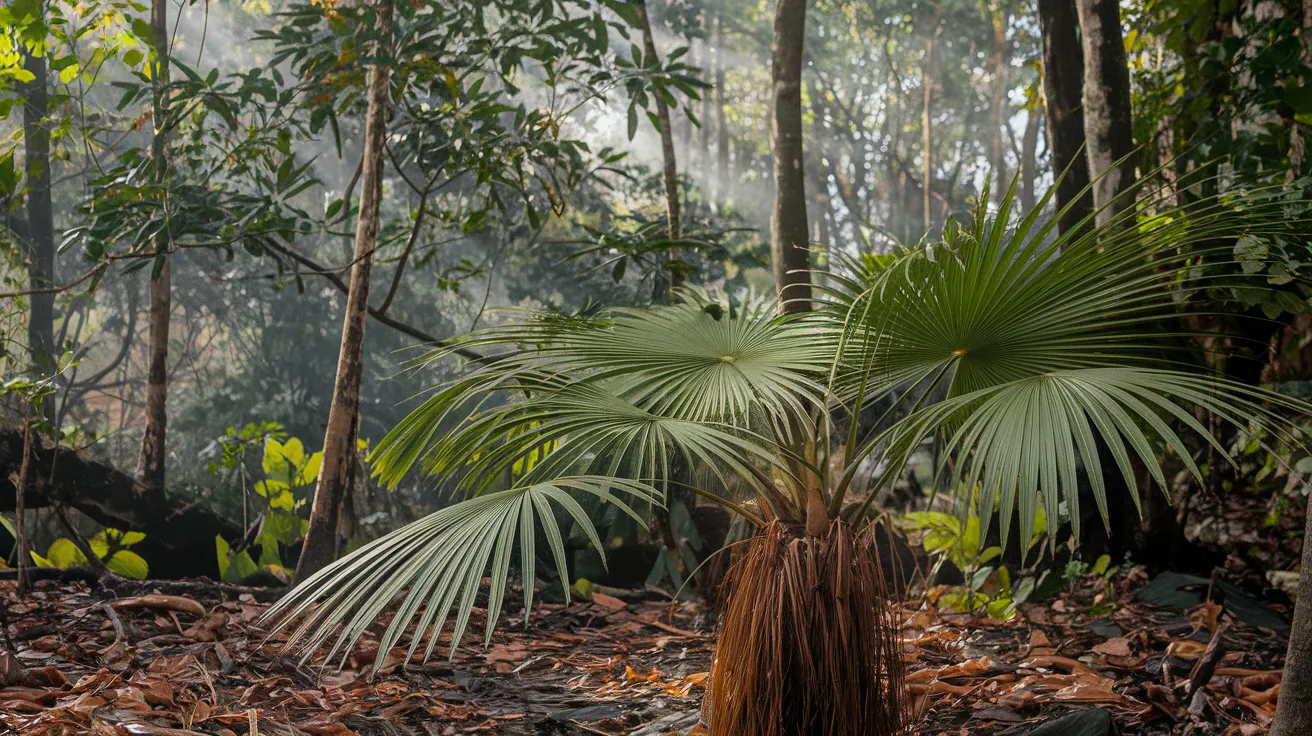

- Interesting Facts: Climbing palm with tough, flexible stems.
- Cultural Significance: Integral to furniture-making in Asia.
- Growth Habits: Climbs trees for sunlight.
- Uses by Humans: Used in furniture and crafts.
11. Mahogany Tree
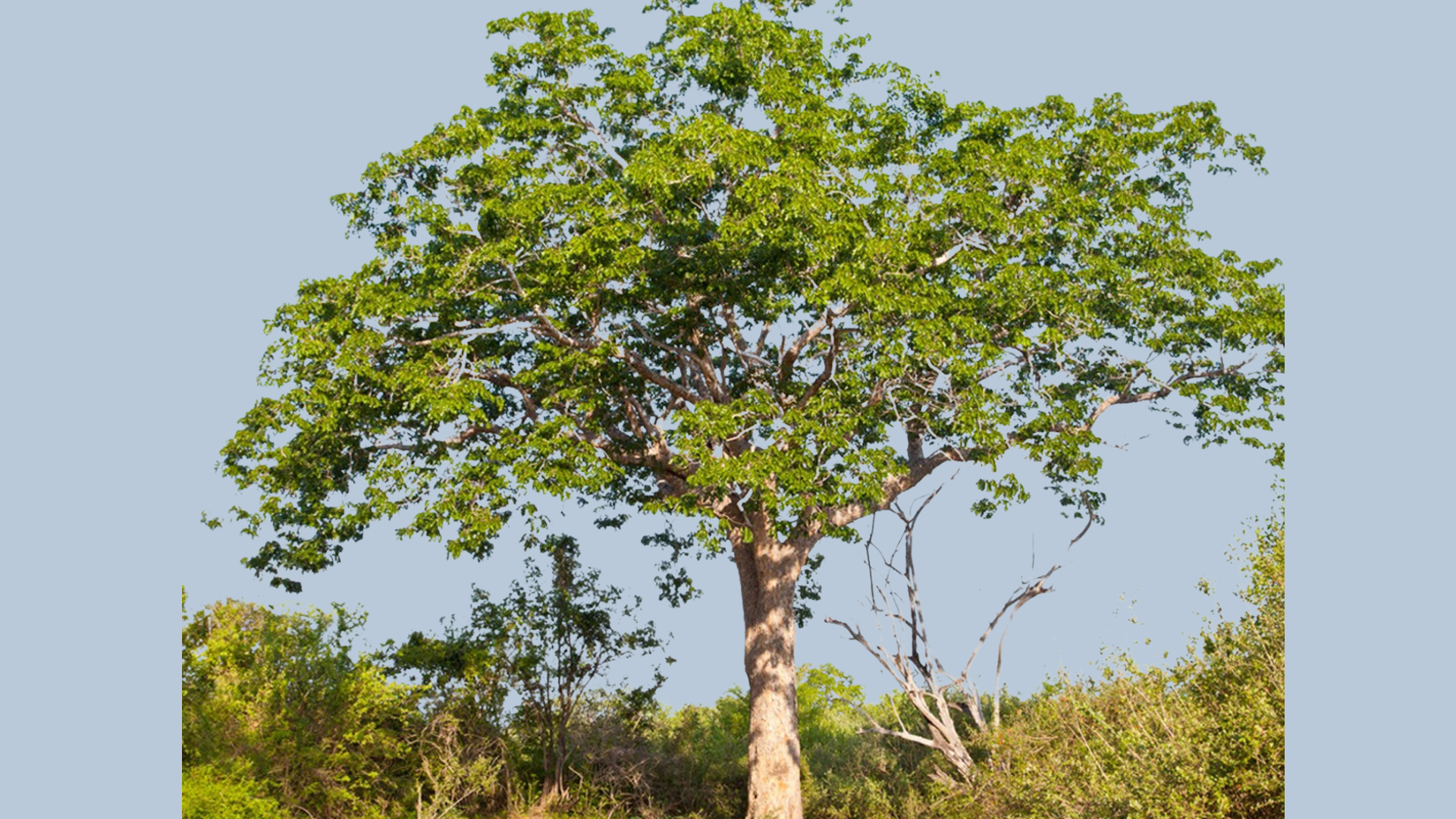

- Interesting Facts: Produces durable, reddish-brown timber.
- Cultural Significance: Symbol of luxury in furniture.
- Growth Habits: Tall, slow-growing hardwood tree.
- Uses by Humans: Timber for furniture and boats.
12. Giant Water Lily
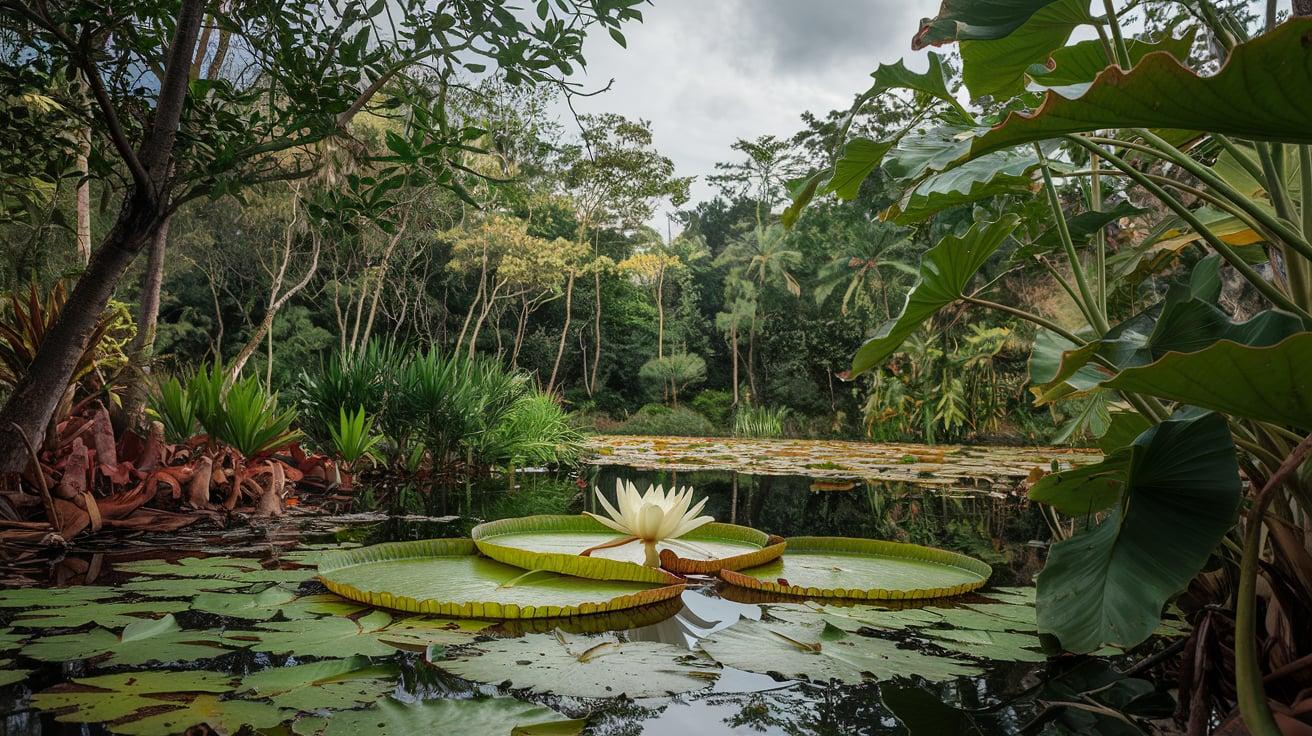

- Interesting Facts: Leaves can support small animals.
- Cultural Significance: National flower of Guyana.
- Growth Habits: Grows in slow-moving water.
- Uses by Humans: Ornamental and symbolic in art.
13. Pitcher Plant
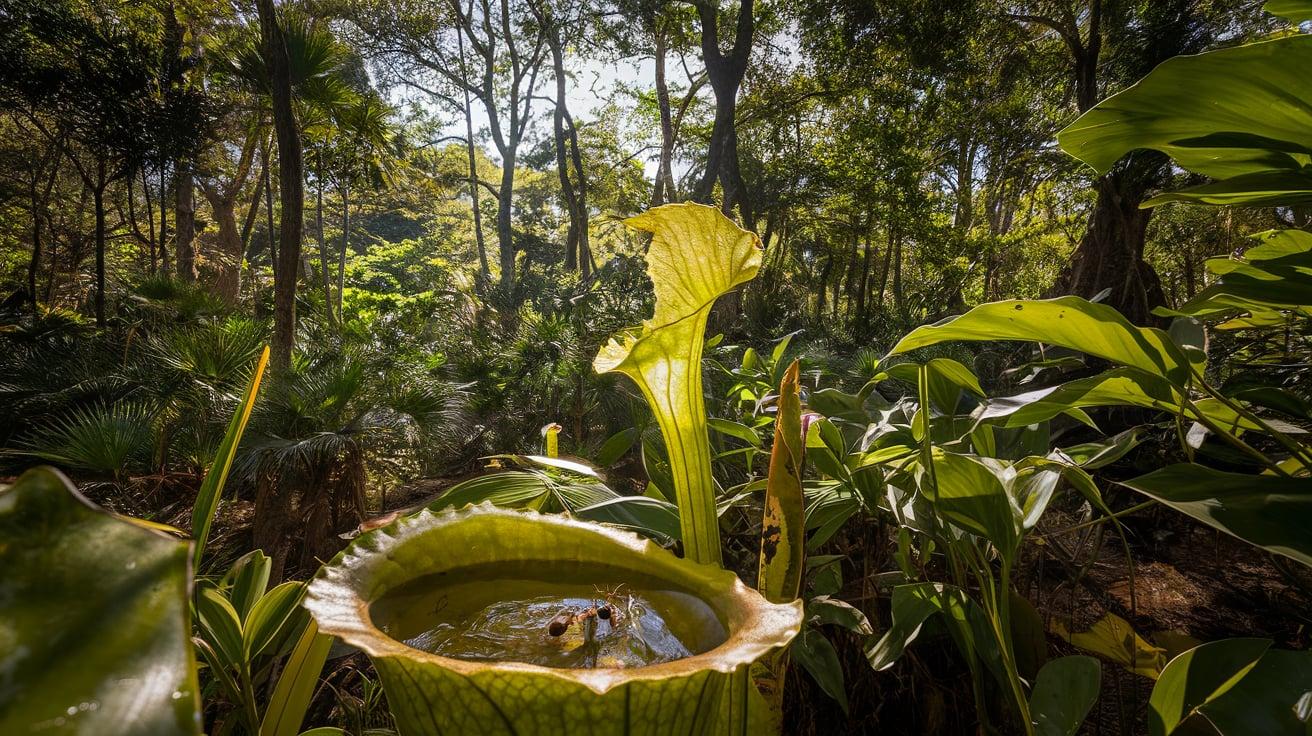

- Interesting Facts: Carnivorous, trapping insects in their “pitchers.”
- Cultural Significance: Represents adaptation in harsh environments.
- Growth Habits: Climbs or grows at ground level.
- Uses by Humans: Studied for biological pest control.
14. Coffee Plant
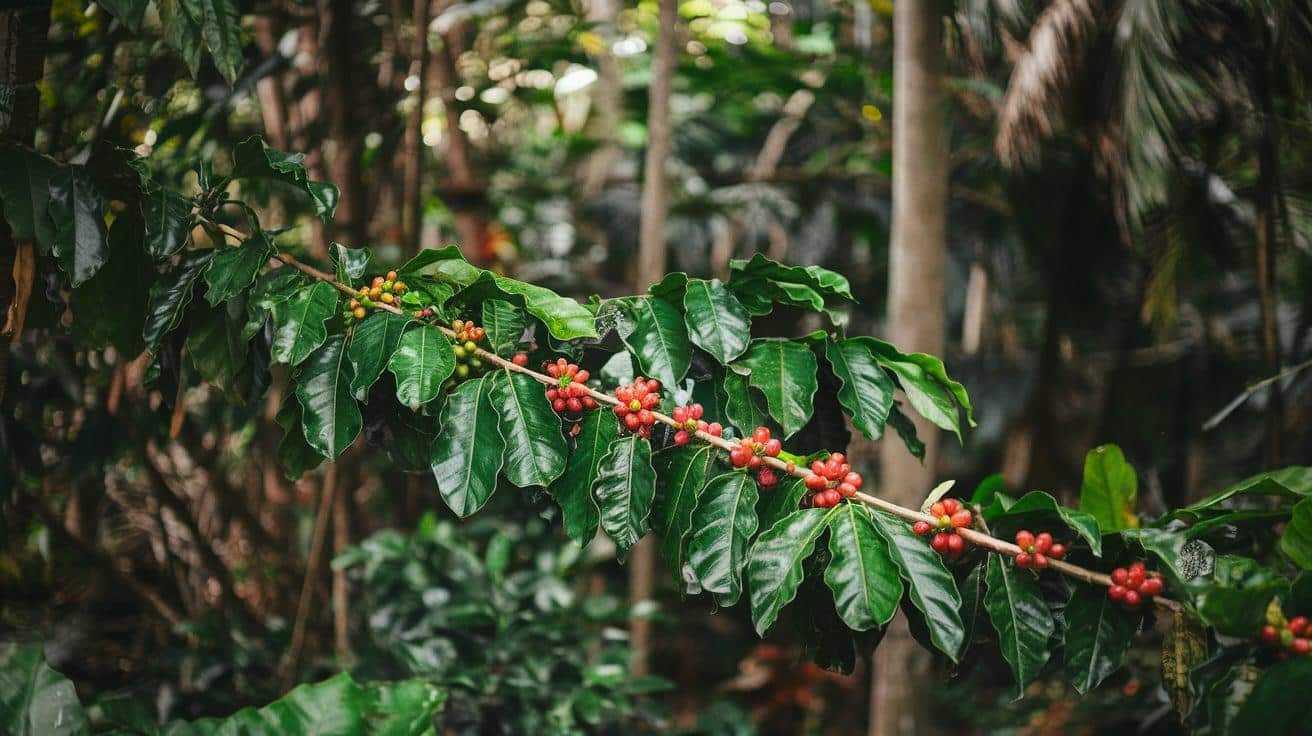

- Interesting Facts: Source of coffee beans.
- Cultural Significance: Coffee culture is central in many societies.
- Growth Habits: Shrubs with glossy leaves.
- Uses by Humans: Beans used for coffee beverages.
15. Balsa Tree
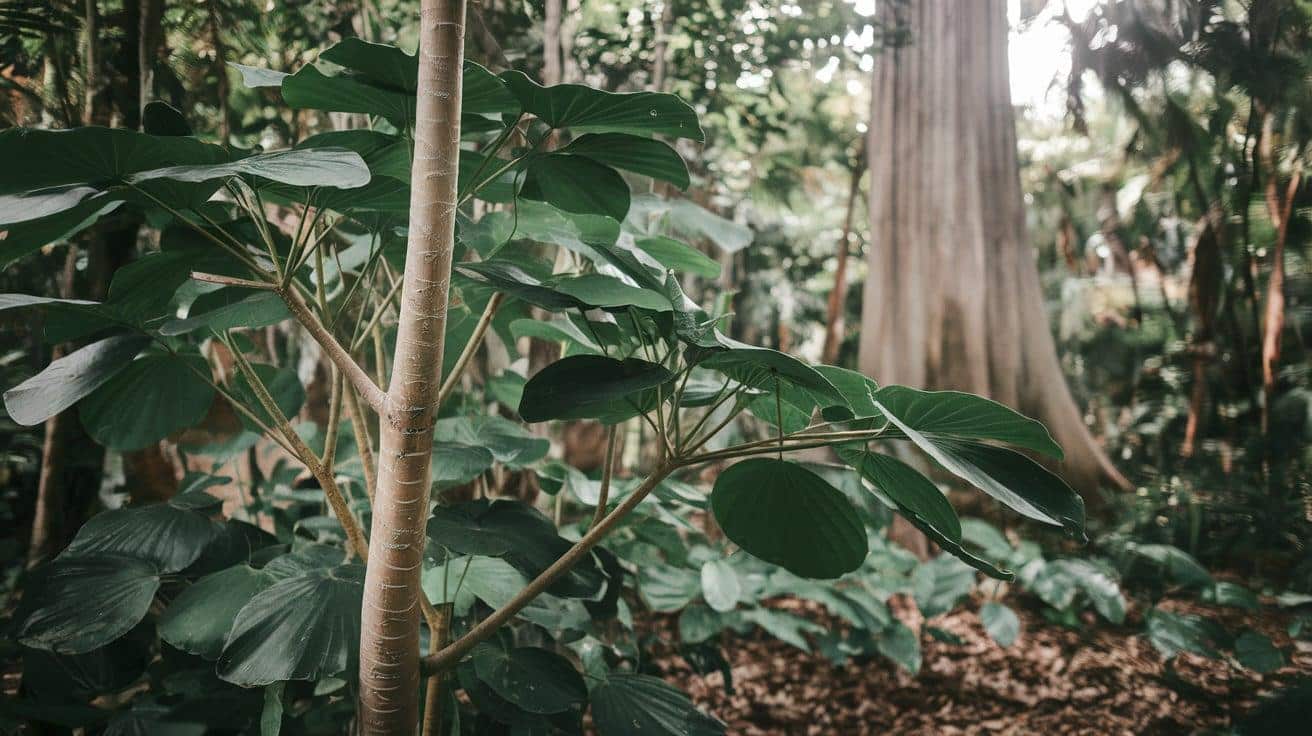

- Interesting Facts: Produces the world’s lightest commercial wood.
- Cultural Significance: Used historically for rafts.
- Growth Habits: Fast-growing, tall tree.
- Uses by Humans: Wood used in crafts and models.
16. Papaya Tree
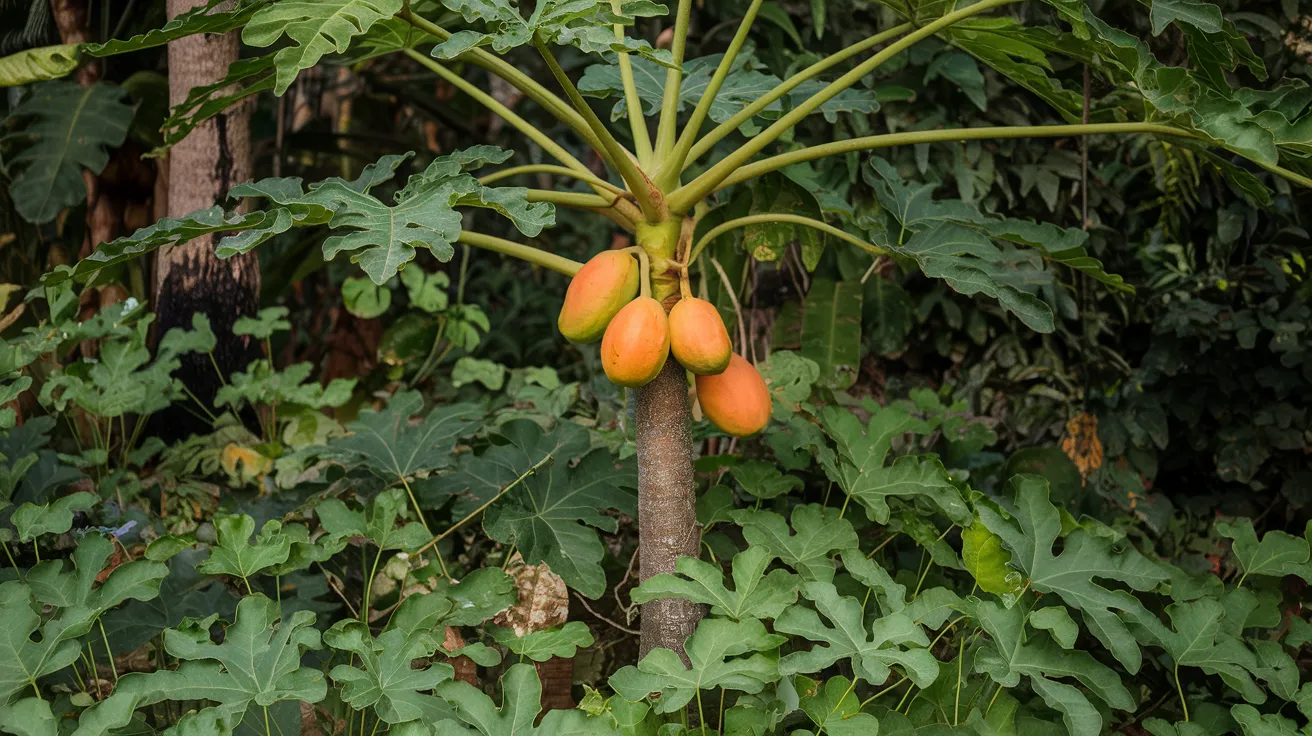

- Interesting Facts: Fruit is rich in vitamins and enzymes.
- Cultural Significance: Important in tropical cuisines.
- Growth Habits: Short-lived, fast-growing tree.
- Uses by Humans: Fruit for consumption; seeds for medicinal use.
17. Brazil Nut Tree
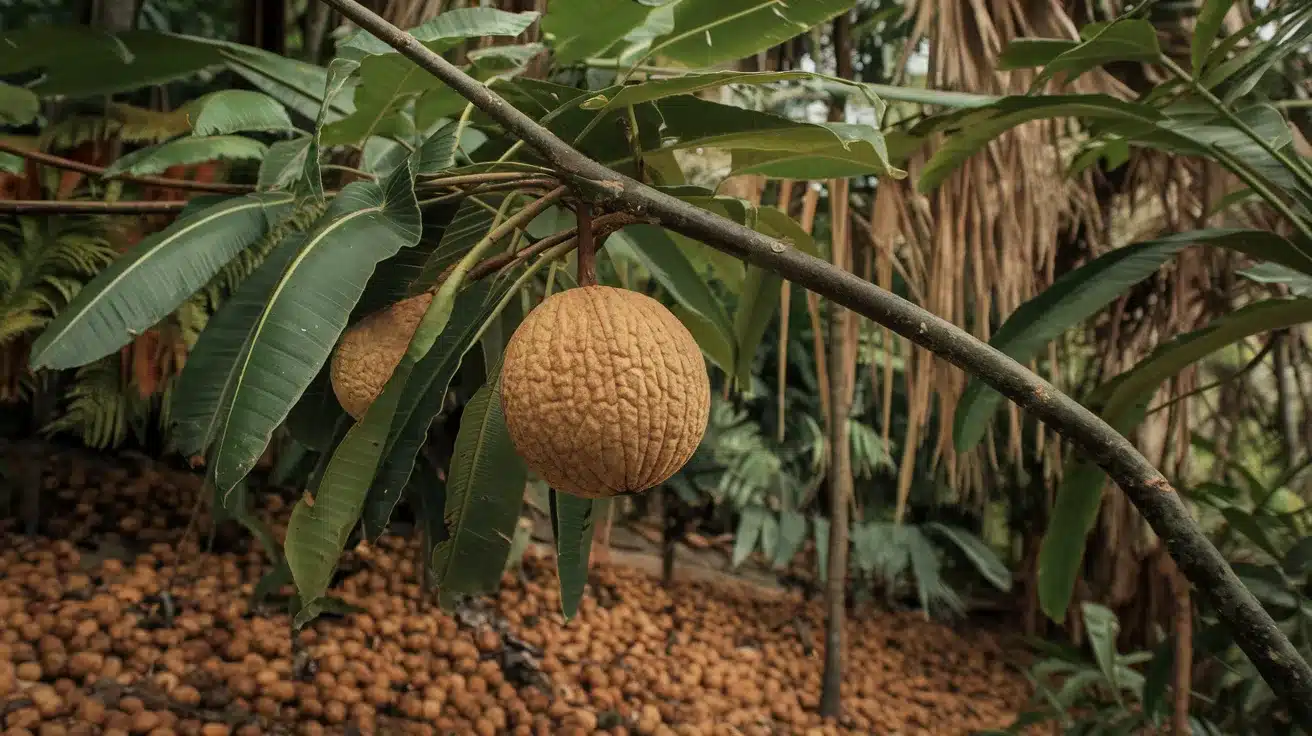

- Interesting Facts: One of the tallest trees in the Amazon.
- Cultural Significance: Economically vital for Amazonian communities.
- Growth Habits: Large canopy tree.
- Uses by Humans: Nuts harvested for food and oil.
18. Vanilla Orchid
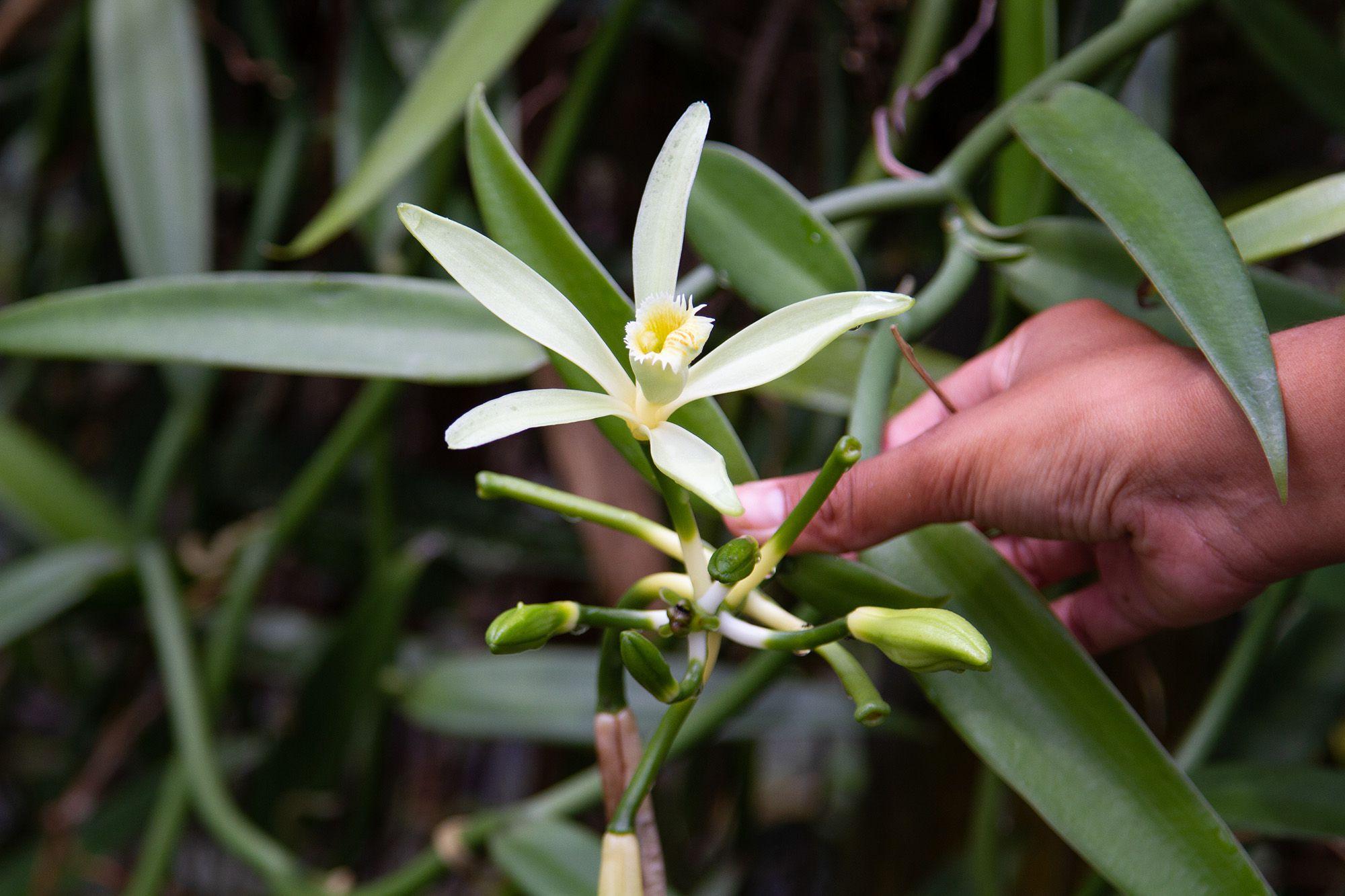

- Interesting Facts: Only orchid that produces edible fruit.
- Cultural Significance: Valued for its flavor and aroma.
- Growth Habits: Climbing Vine.
- Uses by Humans: Pods used in food and cosmetics.
19. Guarana Plant
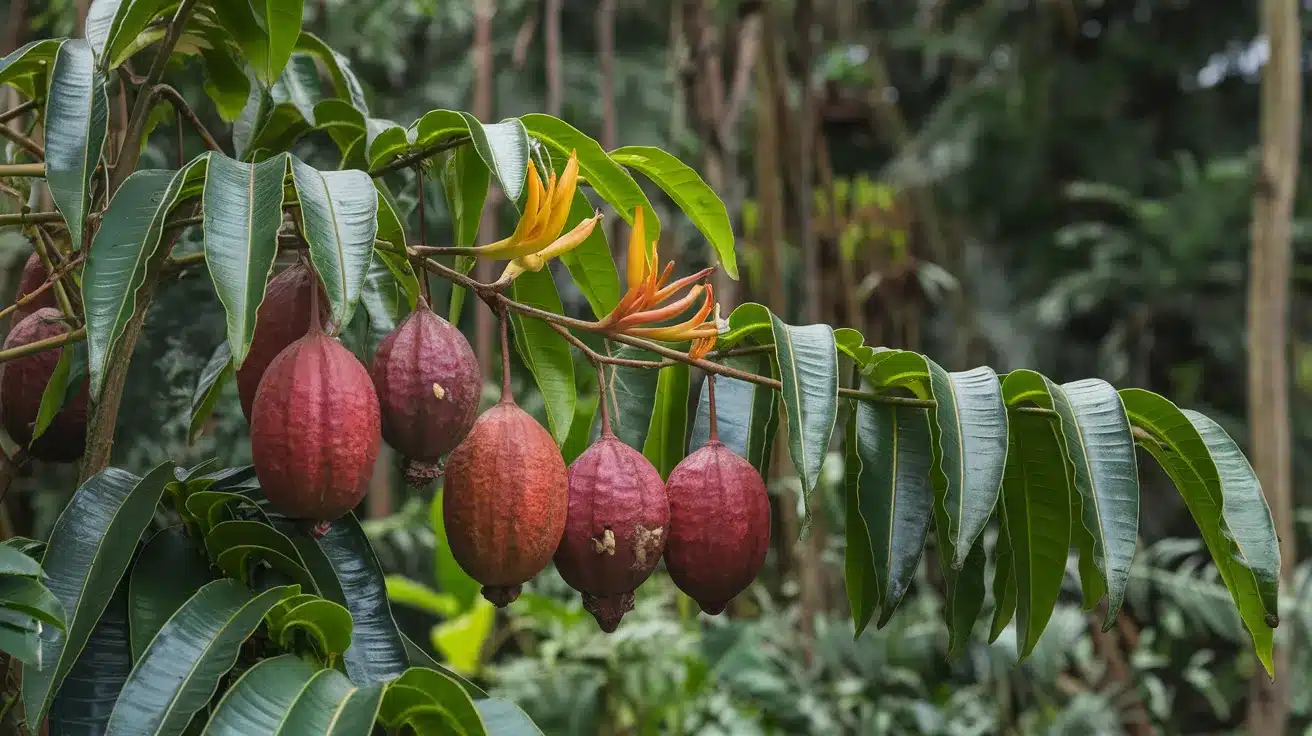

- Interesting Facts: Seeds contain twice the caffeine of coffee beans.
- Cultural Significance: Used by Amazonian tribes for energy.
- Growth Habits: Climbing shrub.
- Uses by Humans: Ingredient in energy drinks and supplements.
20. Ceiba Tree

- Interesting Facts: Known for massive trunks and silky fibers.
- Cultural Significance: Sacred in various cultures, representing the world tree.
- Growth Habits: Large canopy tree.
- Uses by Humans: Wood for canoes; fibers for stuffing.
21. Durian Tree
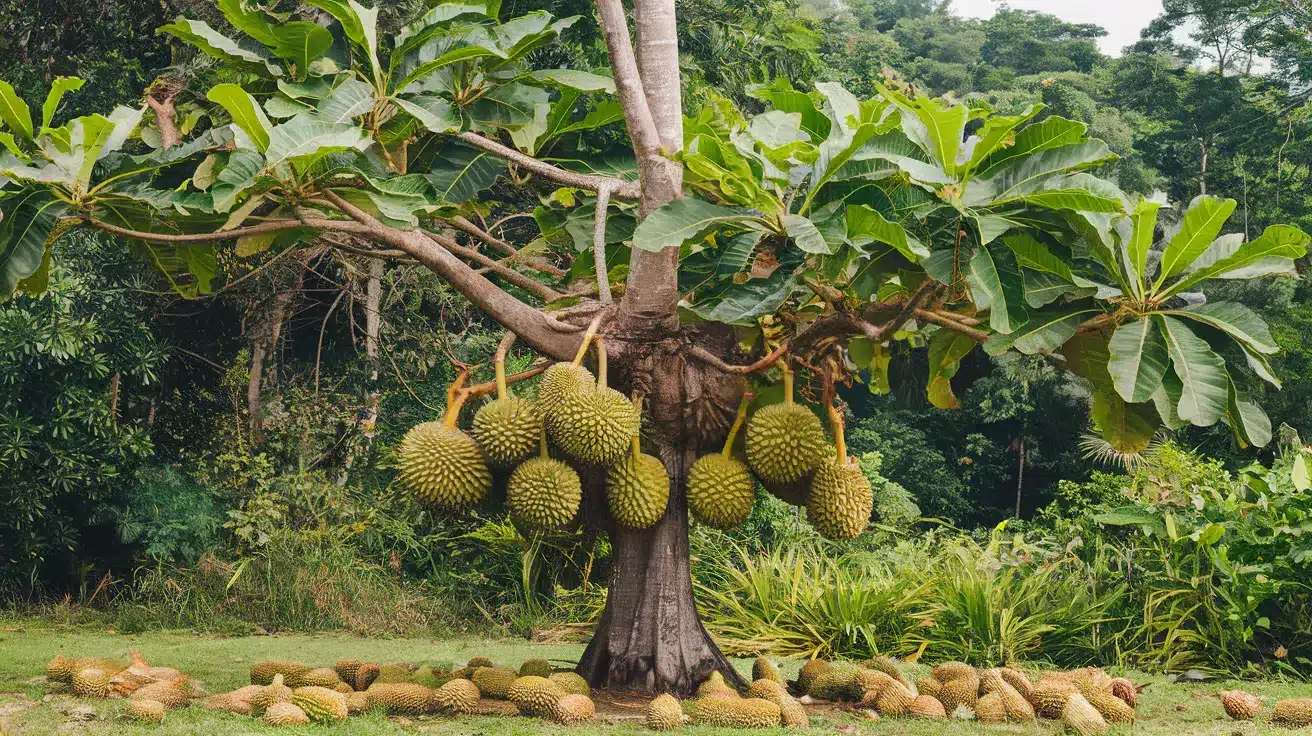

- Interesting Facts: Produces “the king of fruits” with a strong odor.
- Cultural Significance: Culinary delicacy in Southeast Asia.
- Growth Habits: Tall tree with thorny fruit.
- Uses by Humans: Fruit consumed fresh and in desserts.
22. Jackfruit Tree
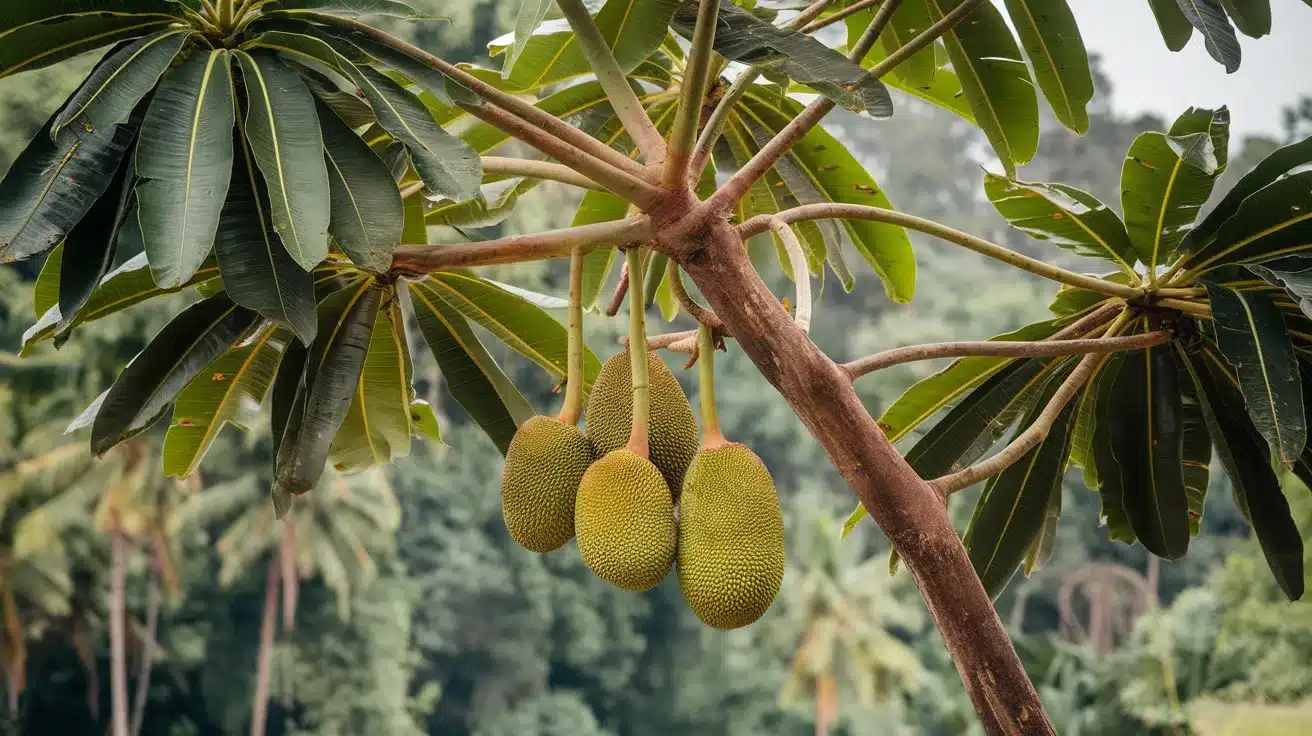

- Interesting Facts: Produces the world’s largest tree-borne fruit.
- Cultural Significance: Staple in South and Southeast Asian cuisines.
- Growth Habits: Evergreen tree.
- Uses by Humans: Fruit is used in cooking; wood is used for furniture.
23. Mangrove Trees
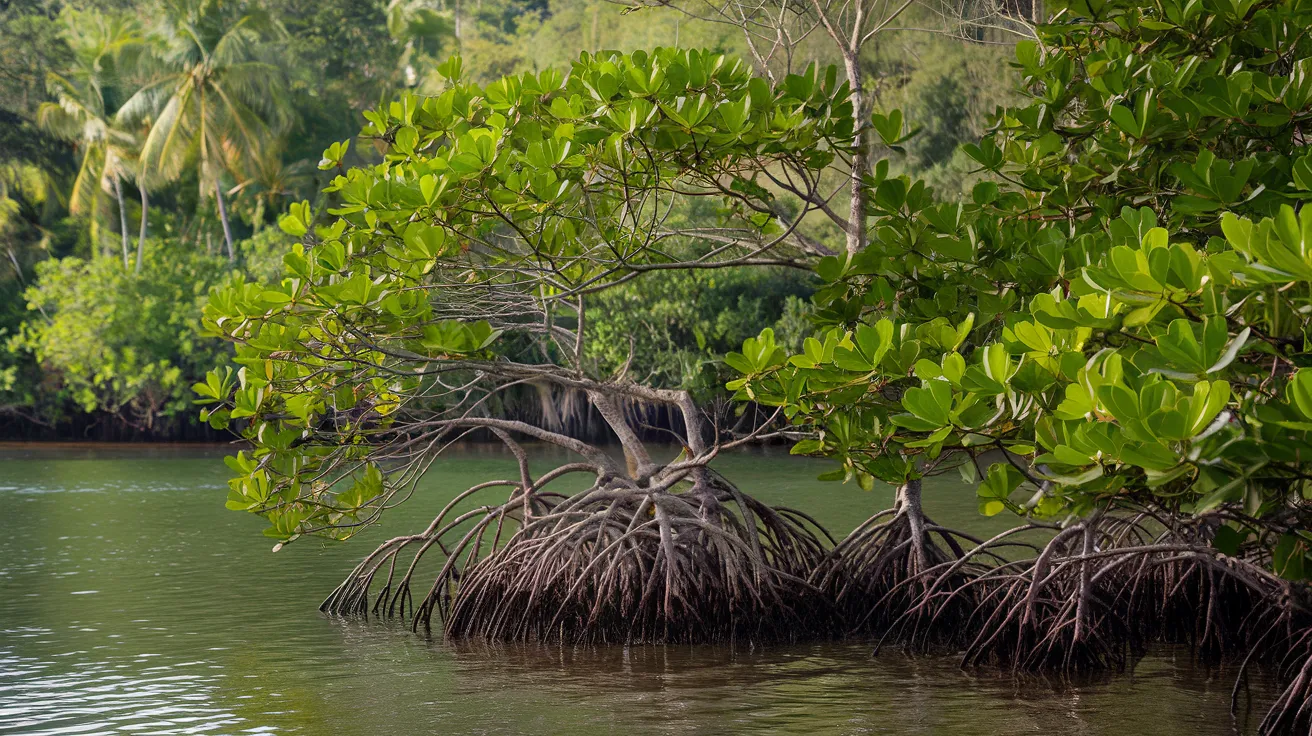

- Interesting Facts: Thrive in salty coastal waters.
- Cultural Significance: Vital for coastal protection.
- Growth Habits: Have aerial roots for oxygen intake.
- Uses by Humans: Wood for construction; roots stabilize coastlines.
24. Tualang Tree
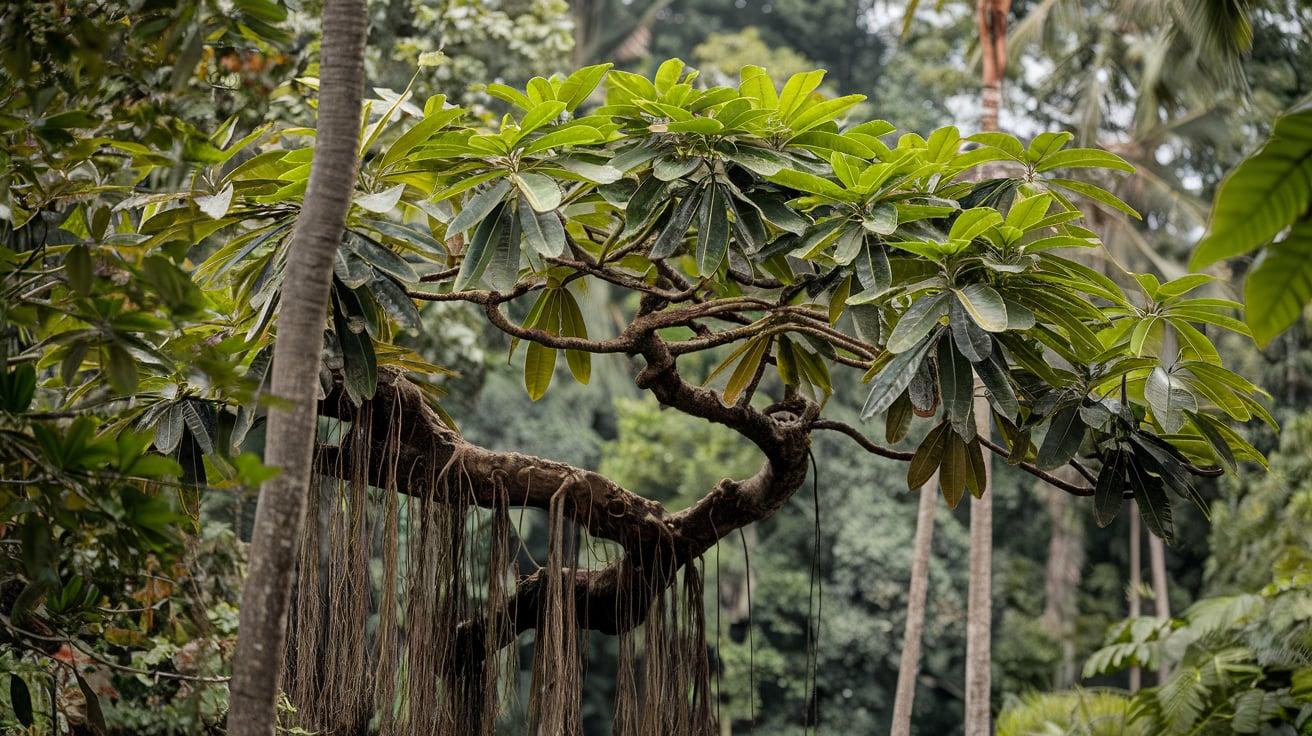

- Interesting Facts: Home to giant honeybee hives.
- Cultural Significance: Source of prized wild honey.
- Growth Habits: Tall tree with smooth bark.
- Uses by Humans: Honey is harvested, and wood is used in construction.
25. Bamboo
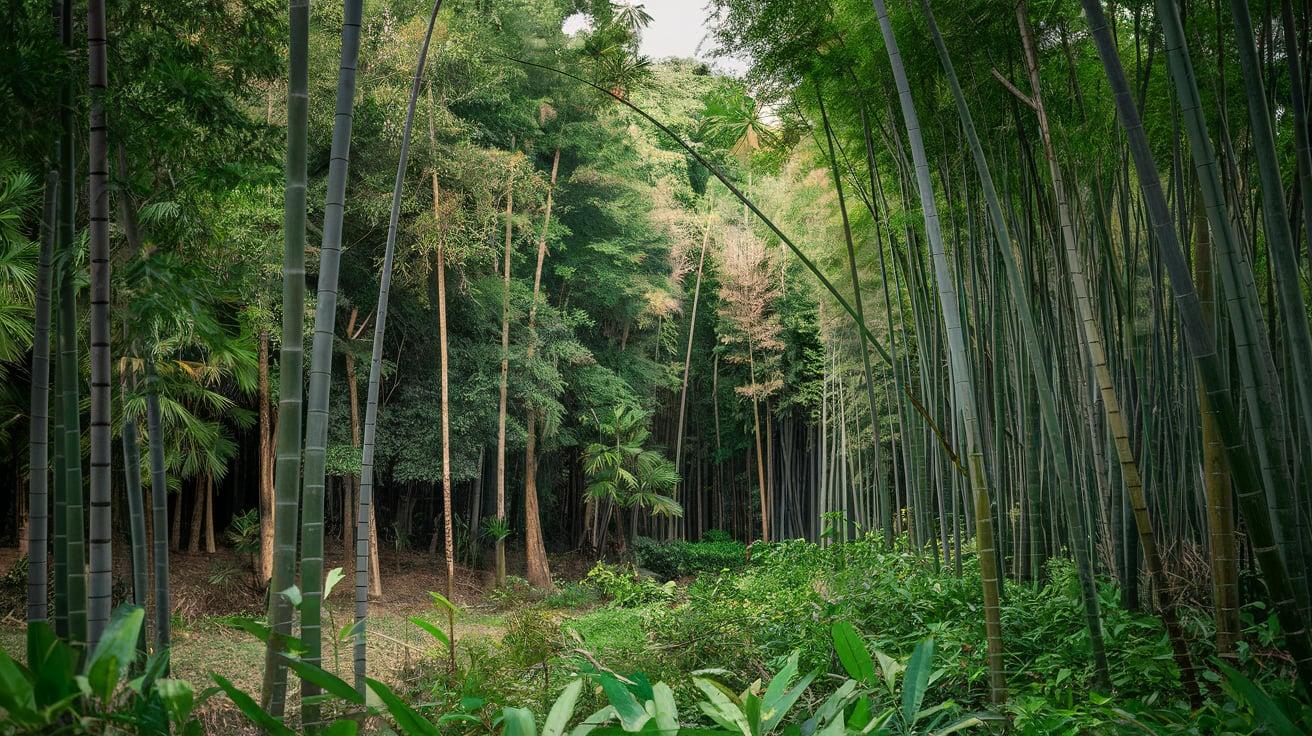

- Interesting Facts: Fastest-growing plant in the world.
- Cultural Significance: Symbol of strength in many Asian cultures.
- Growth Habits: Tall, woody grass.
- Uses by Humans: Used in construction, crafts, and food.
26. Sapodilla Tree
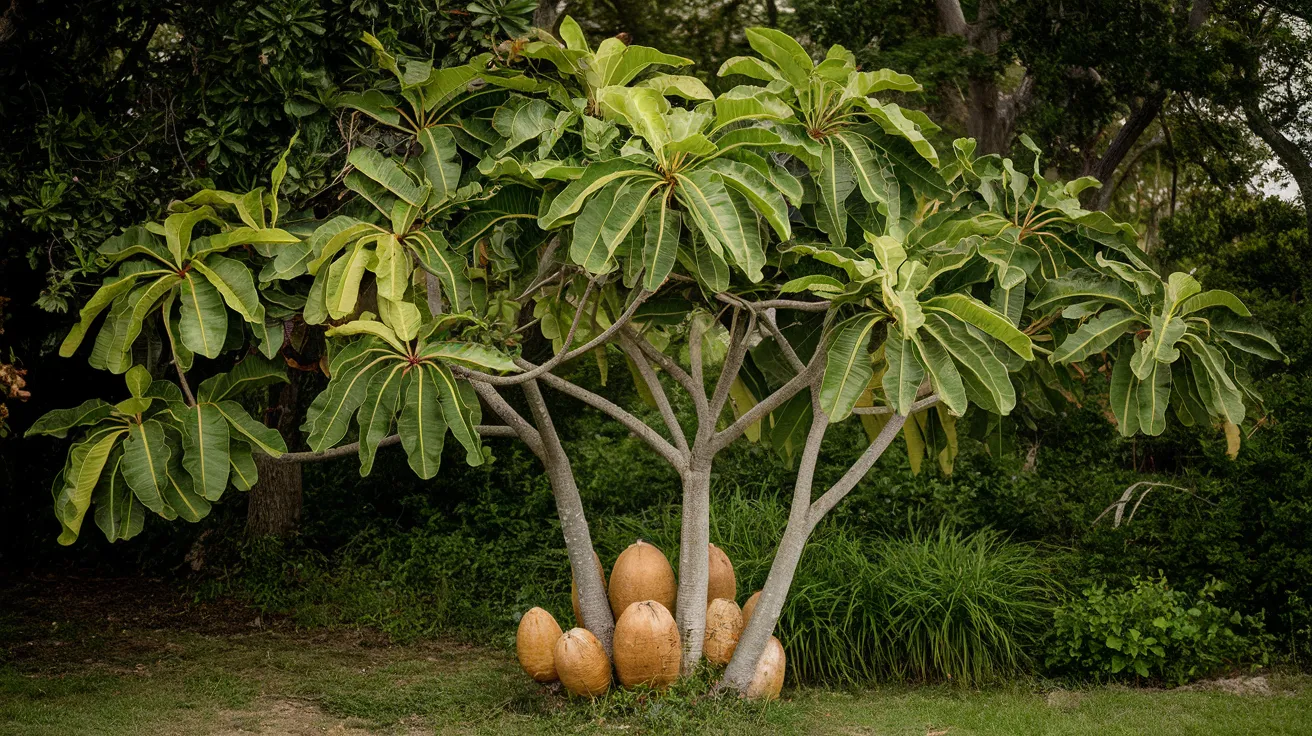

- Interesting Facts: The source of chicle is used in chewing gum.
- Cultural Significance: Valued for its sweet fruit.
- Growth Habits: Medium-sized evergreen trees
- Uses by Humans: Fruit for consumption; chicle for gum.
27. Coconut Palm
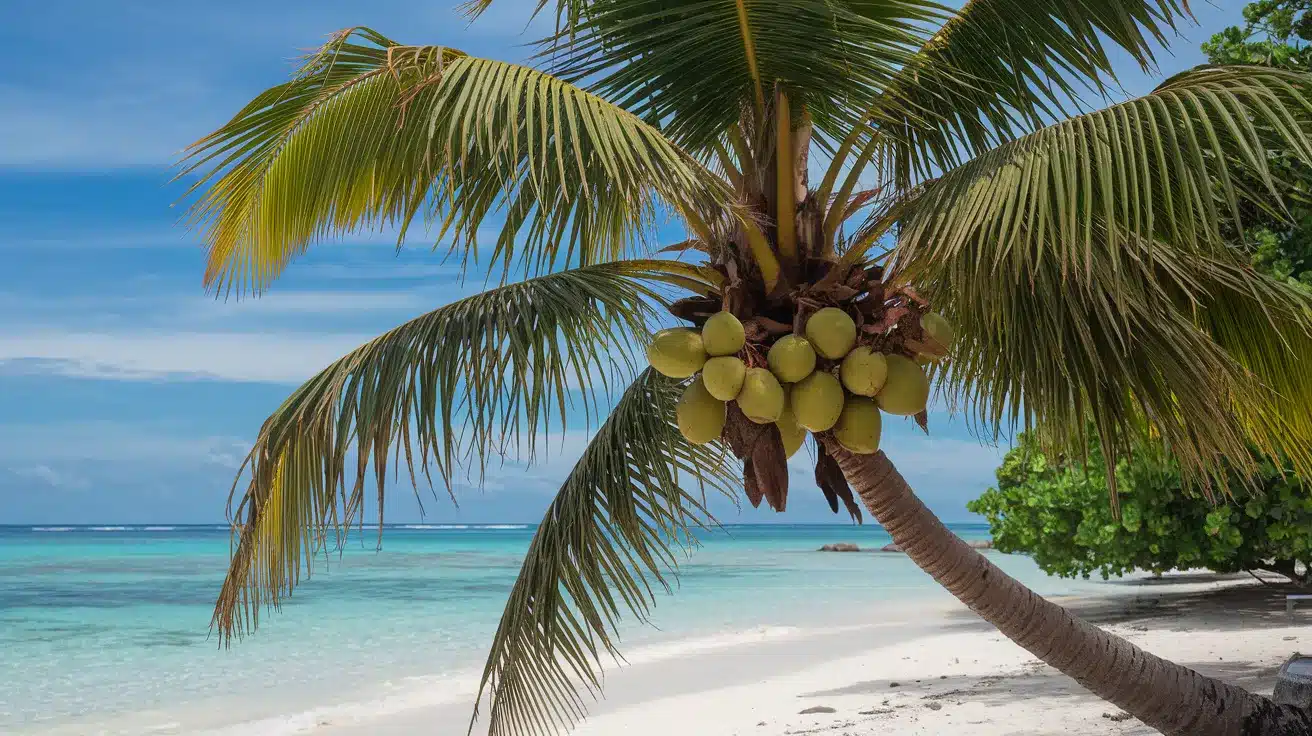

- Interesting Facts: It is called the “Tree of Life” for its versatility.
- Cultural Significance: Integral to many tropical cultures.
- Growth Habits: Tall palm with large leaves.
- Uses by Humans: Provides food, water, oil, and building materials.
28. Ylang-Ylang Tree
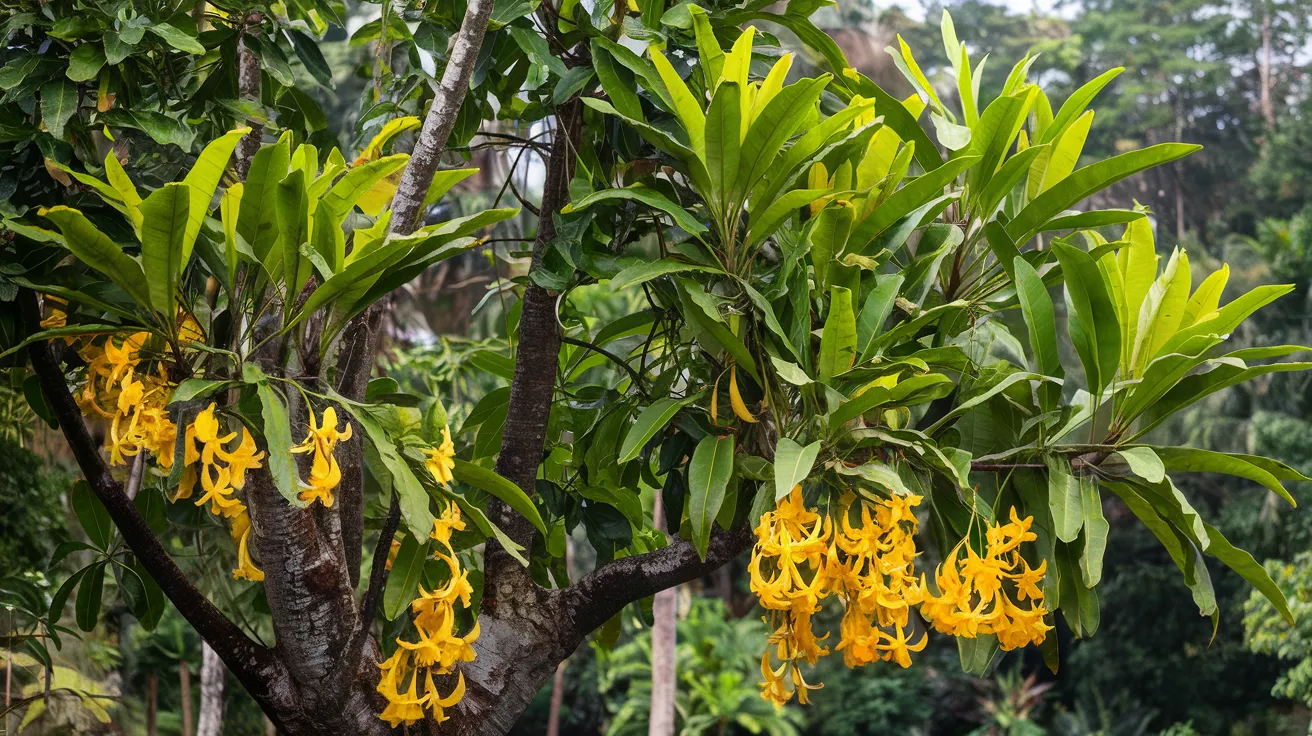

- Interesting Facts: Flowers have a powerful fragrance.
- Cultural Significance: Used in perfumes, including Chanel No. 5.
- Growth Habits: Medium-sized tree with drooping branches.
- Uses by Humans: Flowers for essential oils and perfumes.
29. Rosewood Tree
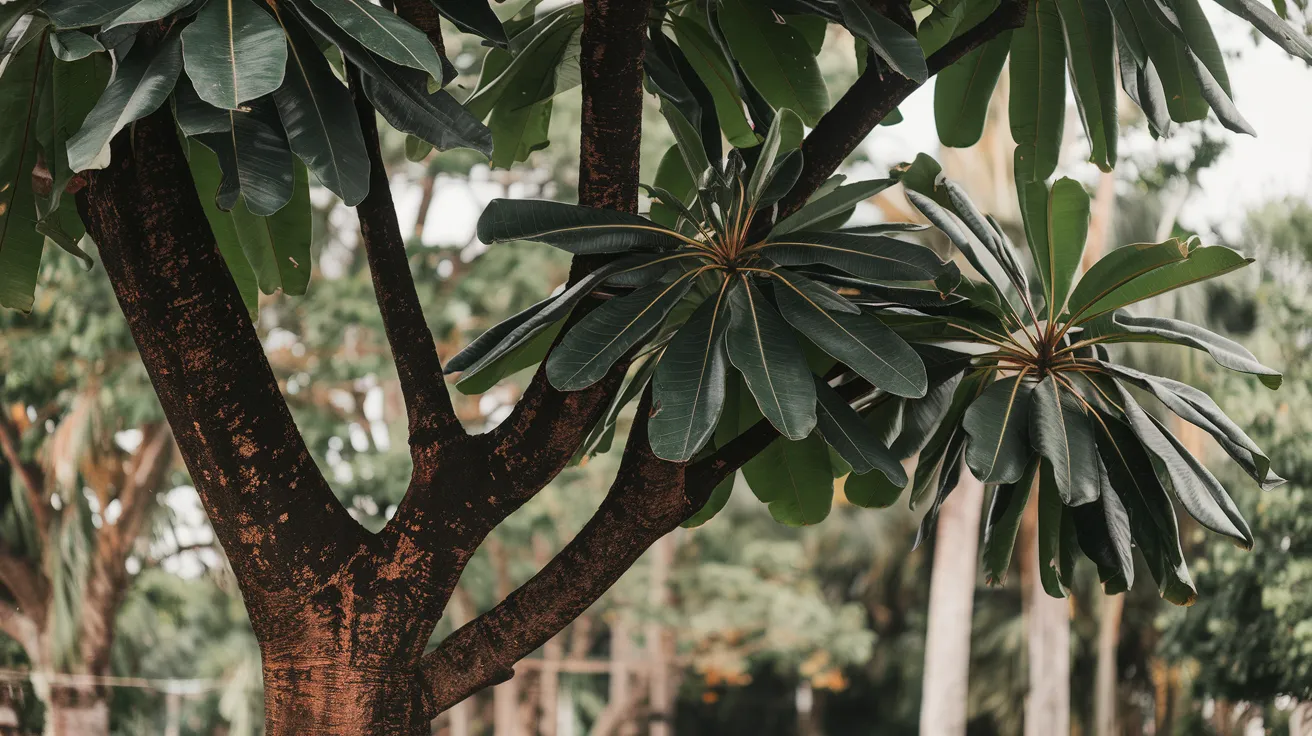

- Interesting Facts: Produces richly colored, fragrant wood.
- Cultural Significance: Symbol of luxury and quality.
- Growth Habits: Slow-growing hardwood tree.
- Uses by Humans: Wood used in furniture and musical instruments.
30. Soursop Tree
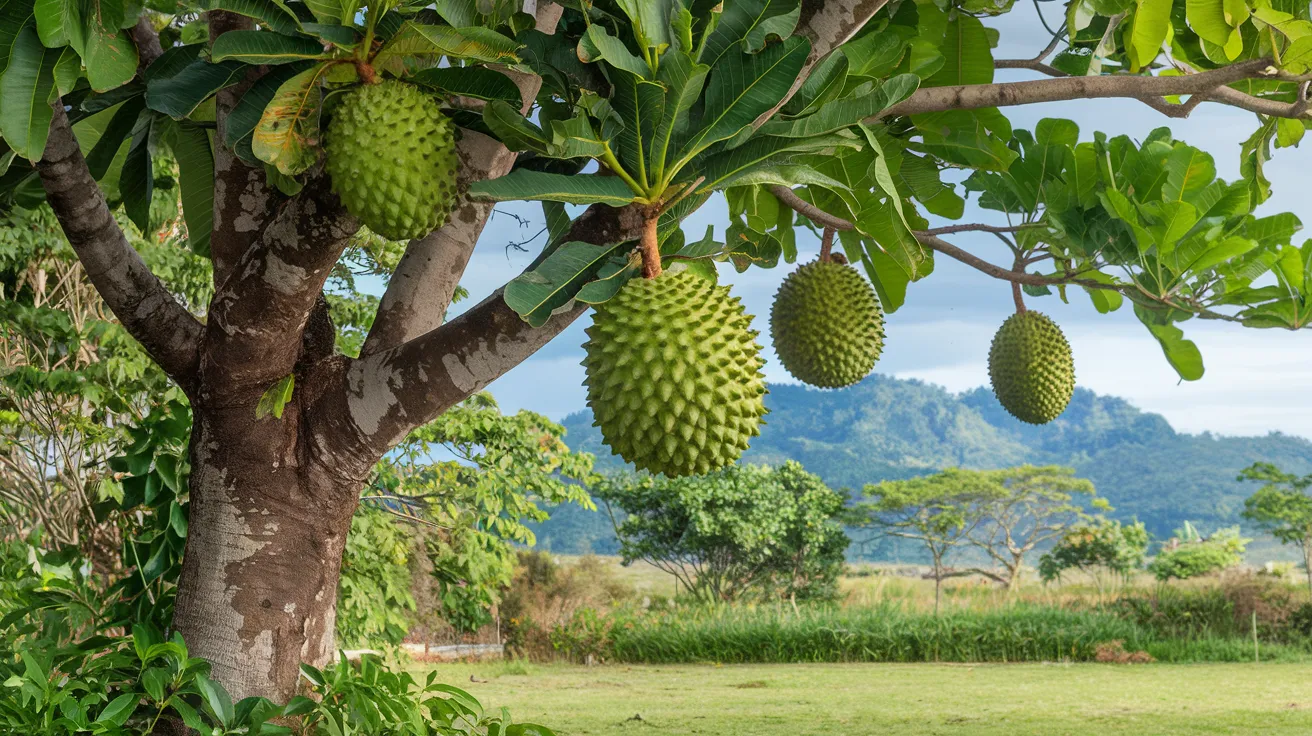

- Interesting Facts: Fruit has a flavor similar to pineapple and strawberry.
- Cultural Significance: Used in traditional medicine.
- Growth Habits: Small, fast-growing tree.
- Uses by Humans: Fruit consumed fresh or in beverages.
31. Neem Tree

- Interesting Facts: Known for its medicinal properties.
- Cultural Significance: Sacred in Indian culture, symbolizing health.
- Growth Habits: Drought-resistant evergreen tree.
- Uses by Humans: Used in medicine, cosmetics, and pesticides.
32. Dragon Blood Tree
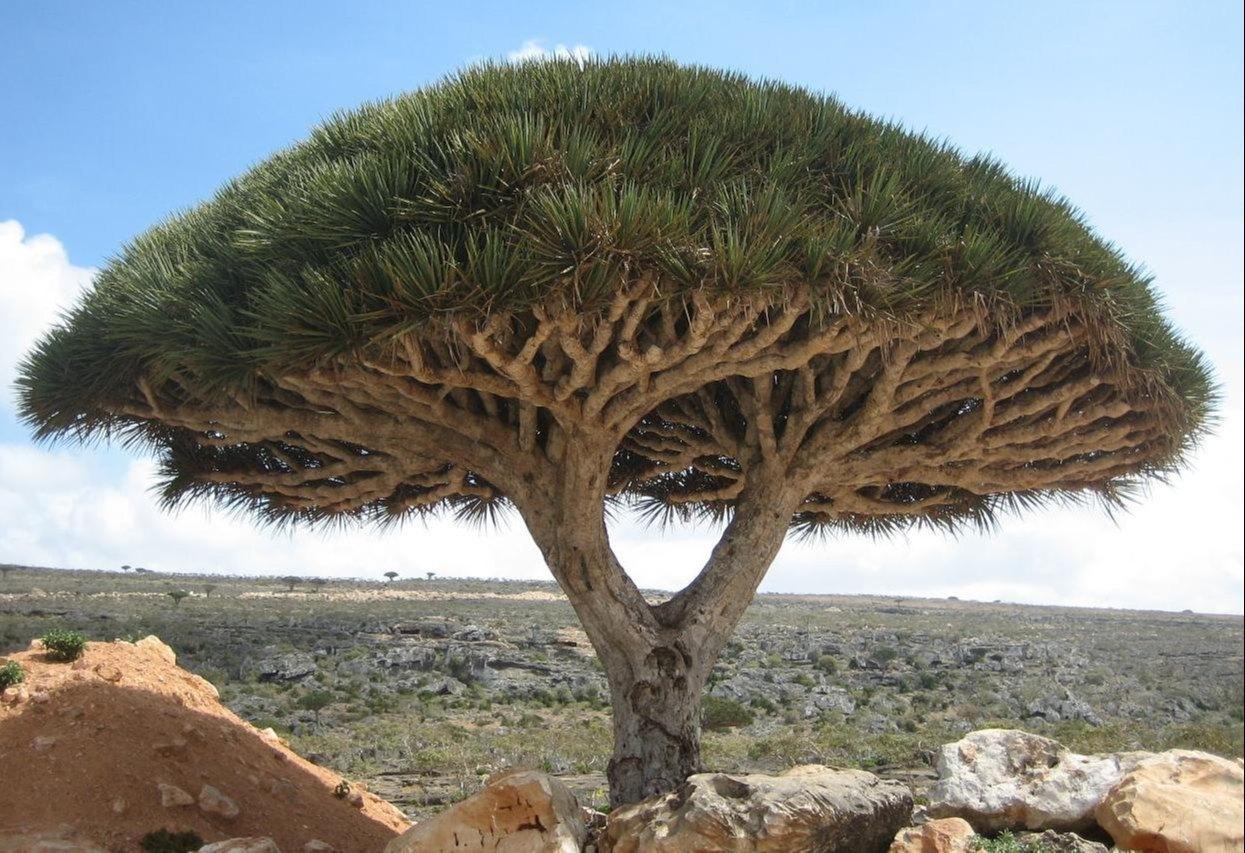

- Interesting Facts: Red sap is used historically as dye and medicine.
- Cultural Significance: Considered mystical in ancient cultures.
- Growth Habits: Umbrella-shaped tree with a dense crown.
- Uses by Humans: Sap is used in varnish and traditional remedies.
33. Torch Ginger
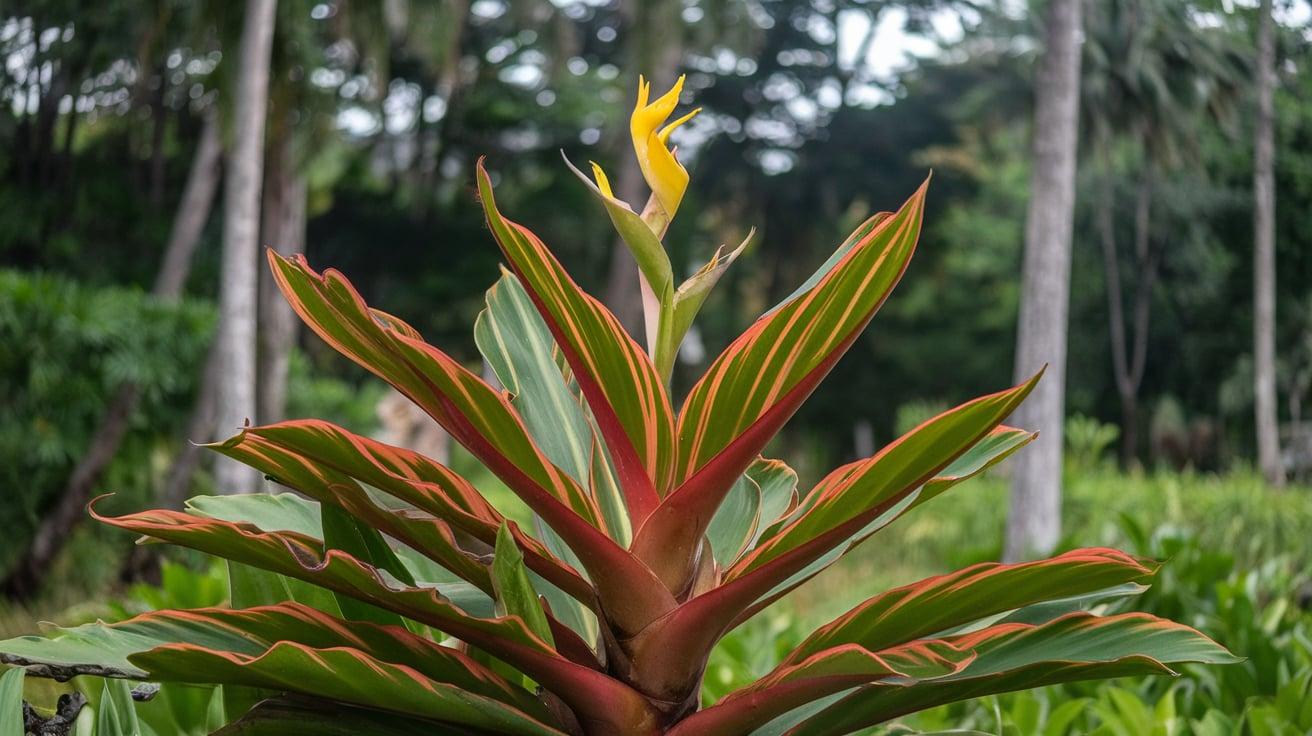

- Interesting Facts: Bright red flower with a striking appearance.
- Cultural Significance: Used in Southeast Asian cuisine and ceremonies.
- Growth Habits: Tall plant with large flower heads.
- Uses by Humans: Edible flower buds are used in cooking; they are ornamental plants.
How Do Tropical Rainforest Plants Contribute to Biodiversity?
Tropical rainforest plants are the true heroes of biodiversity. These green wonders aren’t just pretty—they’re essential for life.
Every plant is vital, from towering trees that form protective canopies to tiny ground plants that enrich the soil.
They provide homes for exotic birds, colorful insects, and rare mammals. Their fruits and flowers feed countless species, while their roots hold the earth together and prevent erosion.
Some even have secret superpowers—like trapping insects or storing rainwater for thirsty creatures. Plus, these plants clean the air, producing oxygen and absorbing carbon dioxide.
Without them, the rainforest wouldn’t buzz, bloom, or breathe.
In short, tropical rainforest plants keep the ecosystem alive, balanced, and bursting with life.
Conclusion
Each leaf, vine, and flower is vital in keeping our planet alive and thriving.
Tropical rainforest plants do more than fill our world with green – they’re the Earth’s life-support system.
From cleaning our air to providing medicine, these remarkable species prove that nature’s simplest forms often hold the most power.
Now you know why scientists work so hard to protect every leaf and stem in these forests.
Every plant in the rainforest, from the smallest seedling to the tallest tree, plays a crucial role in the future of our planet.